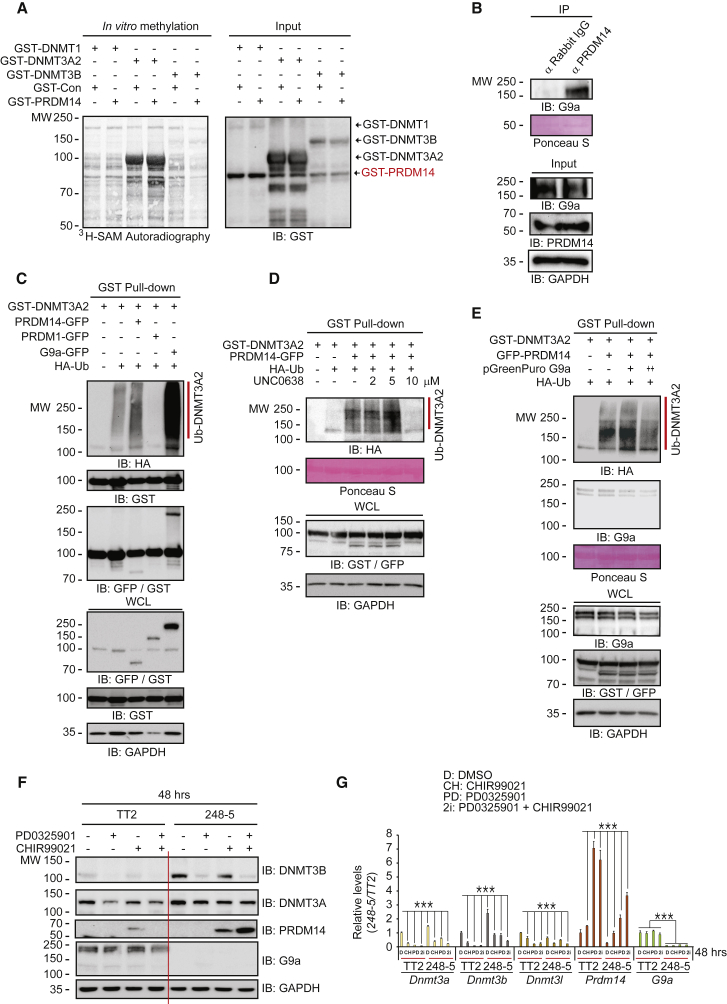
Figure 5.
PDRM14-Mediated G9a/DNMT3A Complex Formation Promotes DNMT3A Protein Degradation
(A) DNMT1, DNMT3A2, and DNMT3B in vitro PRDM14 methyltransferase assay shows that PRDM14 has no methyltransferase activity toward the DNMT family.
(B) Immunoprecipitation assay shows that endogenous PRDM14 associates with G9a.
(C) DNMT3A2 ubiquitination is proportional to the expression of G9a > PRDM14 > Control > PRDM1.
(D) PRDM14 increases DNMT3A2 ubiquitination, but UNC0638 inhibits PRDM14-mediated DNMT3A2 degradation.
(E) Knockdown of endogenous G9a by the shRNA decreases PRDM14-mediated DNMT3A2 ubiquitination.
(F and G) Knockout of G9a and GLP disrupts 2i-mediated reduction of DNMT3A/B and induction of PRDM14 determined by (F) western blots and (G) qRT-PCR (n = 4 independent experiments) in G9a and GLP double-knockout 248-5 ESCs compared with control TT2 cells. ∗∗∗p < 0.001.