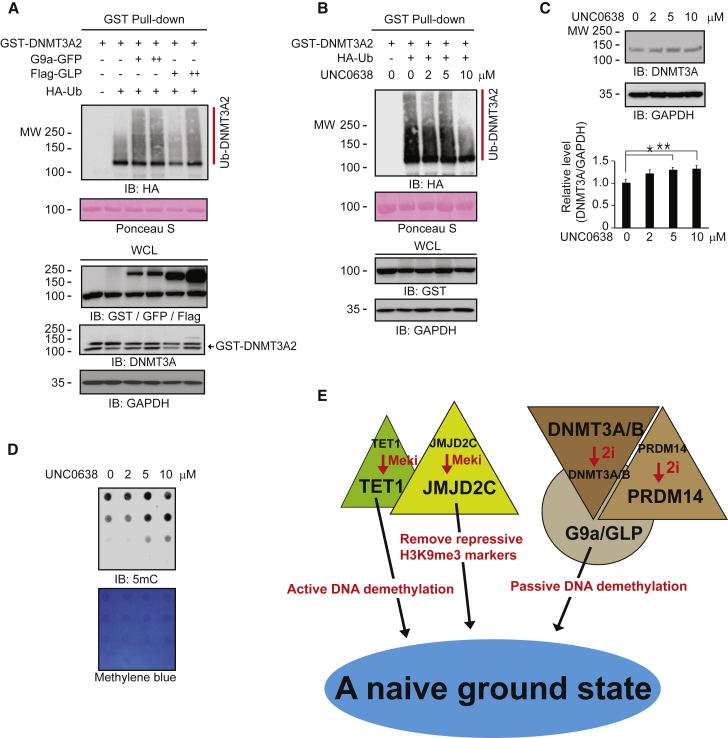
Figure 7.
G9a and GLP Control DNMT3 Degradation in a Methylation-Dependent Manner
(A and B) GST pull-down assays show that (A) GLP and G9a play a key role in DNMT3A2 ubiquitination, and (B) G9a inhibition by the G9a/GLP inhibitor UNC0638 decreases DNMT3A2 ubiquitination.
(C) Western blots show that UNC0638 increases endogenous DNMT3A protein levels in a dose-dependent manner (n = 3 independent experiments).
(D) Dot blots show that G9a inhibition by UNC0638 increases DNA methylation levels.
(E) A model showing that the 2i condition maintains ESCs in a naive ground state through two axes of distinct protein complexes: JMJD2C-enhanced TET1 potentiation and PRDM14/G9A-dependent DNMT3A/B protein degradation.
∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01.