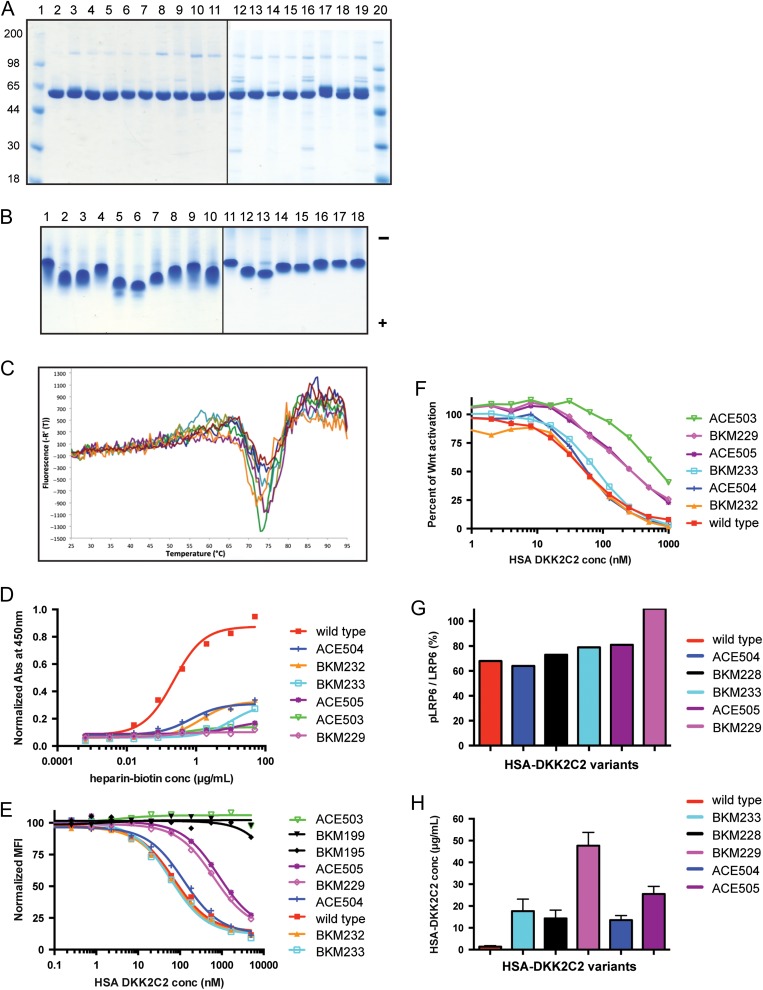
Fig. 4.
Characterization of HSA-DKK2C2 variants. (A) Reducing SDS-PAGE stained with SimplyBlue SafeStain examining purified HSA-DKK2C2 variants. Lanes 1 and 20: molecular weight standards; Lane 2: wild type HSA-DKK2C2 ACE464; Lane 3: BKM225; Lane 4: BKM226; Lane 5: BKM227; Lane 6: BKM228; Lane 7: BKM229; Lane 8: BKM230; Lane 9: BKM231; Lane 10: BKM232; Lane 11: BKM233; Lane 12: ACE502; Lane 13: ACE504; Lane 14: ACE505; Lane 15: ACE506—pH 5.5 purification; Lane 16: ACE506—pH 6.5 purification; Lane 17: ACE507—pH 5.5 purification, glycosylated form; Lane 18: ACE507—pH 5.5 purification, hypo-glycosylated form; Lane 19: ACE507—pH 6.5 purification. (B) Approximately 4 μg of wild-type HSA-DKK2C2 and each of the variants were analyzed by native PAGE under non-reducing conditions and stained with SimplyBlue SafeStain. Lane 1: wild type HSA-DKK2C2 ACE464; Lane 2: BKM225; Lane 3: BKM226; Lane 4: BKM227; Lane 5: BKM228; Lane 6: BKM229; Lane 7: BKM230; Lane 8: BKM231; Lane 9: BKM232; Lane 10: BKM233; Lane 11: ACE502; Lane 12: ACE504; Lane 13: ACE505; Lane 14: ACE506—pH 5.5 purification; Lane 15: ACE506—pH 6.5 purification; Lane 16: ACE507—pH 5.5 purification, glycosylated form; Lane 17: ACE507—pH 5.5 purification, hypo-glycosylated form; Lane 18: ACE507—pH 6.5 purification. Direction of anode (−) and cathode (+) is indicated. (C) A graphical depiction of the DSF profiles of selected HSA-DKK2C2 mutants. Thermal denaturation profiles for the six mutants BKM229 (brown); ACE505 (magenta); BKM228 (cyan); ACE504 (green); ACE506 (orange); and BKM233 (blue), and wild type HSA-DKK2C2 ACE464 (red), from 25°C to 95°C. (D) A graphical depiction of the results of heparin–biotin ELISA for selected HSA-DKK2C2 mutants. Titrations curve for biotin–heparin binding to HSA-DKK2C2 mutants plated at 15 µg/ml. Detection was at 450 nm with streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase. Illustrated is a representative of duplicate experiments for these variants. (E) A graphical depiction of the results of HSA-DKK2C2 mutant competition with anti-LRP6 antibody for binding to LRP6. LRP6 binding curves for HSA-DKK2C2 molecules impaired for either heparin or LRP6 binding (BKM195 and BKM199), following competition with anti-LRP6 monoclonal antibody. (F) A graphical depiction of percent canonical Wnt pathway activation in STF assay by Wnt3a in response to varying concentrations of wild type HSA-DKK2C2 ACE464 (red) and selected HSA-DKK2C2 variants. Plotted are the average values from triplicate experiments. (G) Bar graph depicting the ratio of phosphorylated LRP6 to total LRP6 detected by Western blotting for cells treated with each of the six HSA-DKK2C2 variants. This experiment was performed at three concentrations of DKK2C2 molecule (250, 500 or 1000 nM). Plotted values are depicting values generated from incubation with 1000 nM. (H) PK analysis of HSA-DKK2C2 variants. A bar graph depicting average serum levels from 2 or 3 mice intravenously dosed with 10 mg/kg of HSA-DKK2C2 molecules 24 h postinjection. Variants were detected by quantitative western blotting and quantified against a standard curve of wild type HSA-DKK2C2 ACE464 in serum. In D–H wild type refers to ACE464.