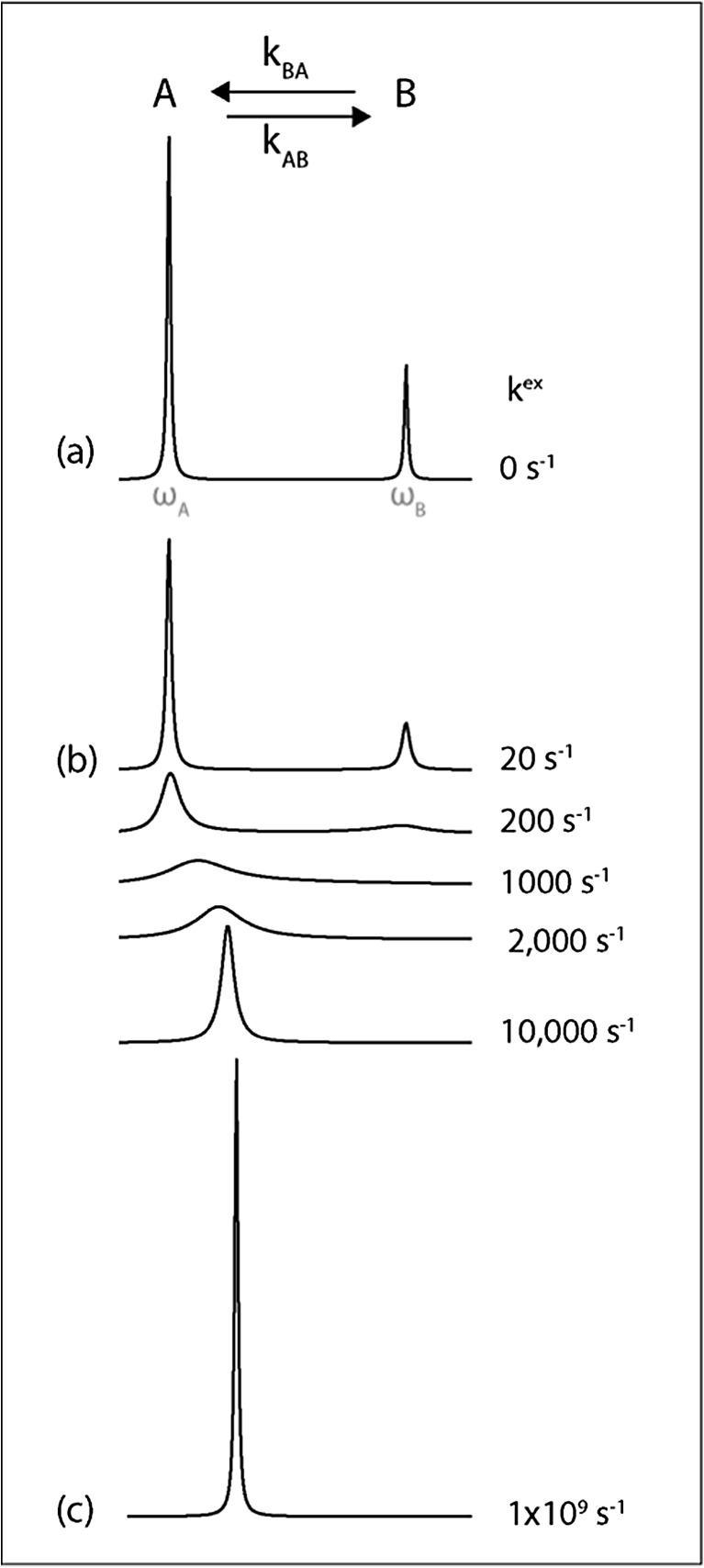
Fig. 2.
Simulated one-dimensional NMR spectra for nuclei exchanging between two distinct chemical environments. a When the rate of exchange is much slower than the difference in chemical shift, separate peaks are observed for the two states. b Exchange broadening is caused by stochastic variations in chemical shift, which cause the NMR signal to decay more rapidly, leading to broader, weaker signals. c When exchange is far more rapid than the difference in chemical shift, a single sharp peak is obtained at the population weighted average chemical shift