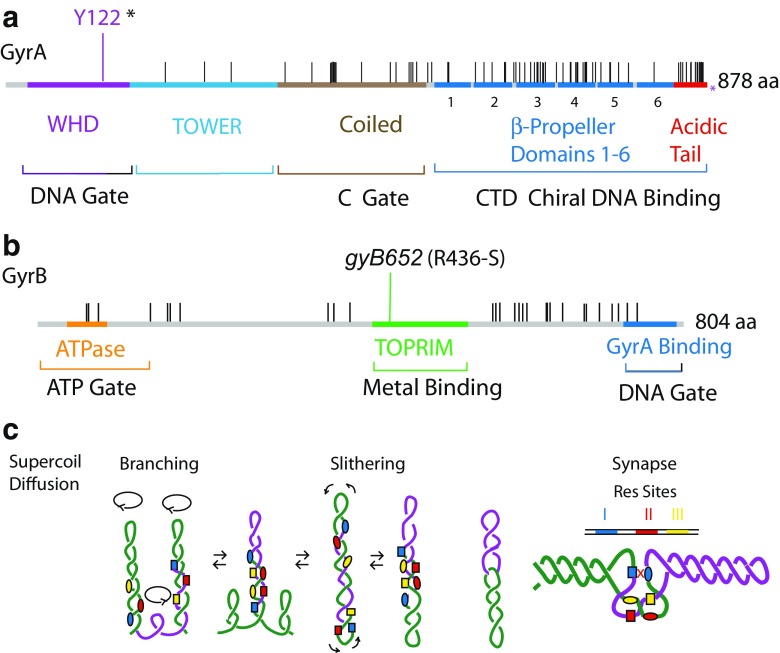
Fig. 1.
Structure and sequence alignment of DNA gyrase A and B genes (GyrA, GyrB) from Salmonella and Escherichia coli. a For GyrA the catalytic tyrosine (Y122) is shown in purple. There are 77 positions with amino acid substitutions between the species (black lines). The reference sequence is Salmonella GyrA, which is 3 amino acids longer than E. coli GyrA and terminates at 875 amino acids. b GyrB is more highly conserved than GyrA, with the two proteins differing at only 28 positions in this 804-amino acid protein. Domains for GyrA include the DNA Gate, the C Gate, and the CTD Chiral DNA Binding elements. For GyrB domains include the ATP Gate, Metal Binding site, and GyrA Gate interaction region. c. Long-range diffusion mechanisms of negative supercoiling is illustrated for a segment of DNA that includes two directly repeated recombination sites for the γδ resolvase (Res). One Res dimer binds to three DNA sites, numbered I (blue), II (red), and III (yellow). Branch extrusion (c, left) or reptilian slithering (c, center) move the two Res sites into a three-node tangle. (c, far right). The products of recombination are two catenated circles (c right). In vivo-catenated links are separated by topoisomerase IV (Topo IV)