Figure 5. Schematic diagram of CRH in MS-induced intestinal injury.
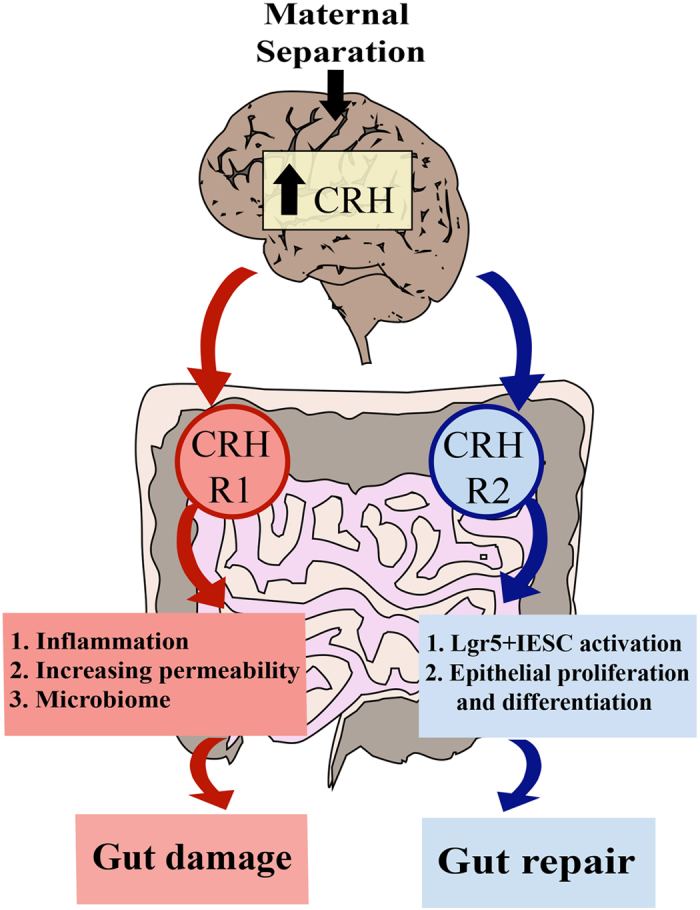
Schematic diagram illustrating the role of CRH in the brain-gut axis, which is critical for the induction of colonic injury caused by maternal separation. We suggest that maternal separation is associated with an increase in CRH secretion by the hypothalamus. CRH binds to CRHR1 and CRHR2, which have opposing effects. CRHR1 is involved in the initiation of gut damage, through increased inflammation, permeability and alterations of the microbiome. CRHR2 is involved in intestinal injury repair by activating Lgr5+ IESCs and promoting epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation.
