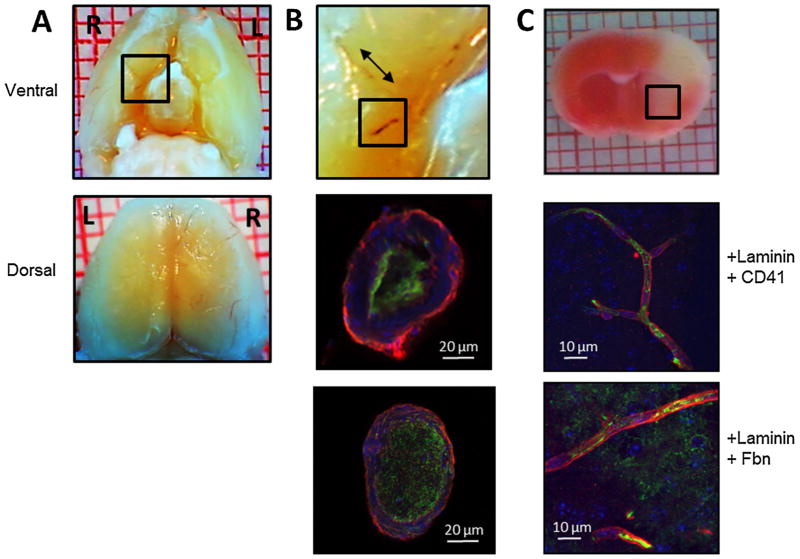
Fig. 3.
Collagen injection causes formation of platelet- and fibrin-rich thrombi in cerebral macro- and microvessels. Focal cerebral ischemia was induced by injecting six 1-μg boluses of collagen into the distal right internal carotid artery (ICA) of the mouse. Three hours after collagen injection, brains were excised for histologic and immunofluorescent examination of cerebral vasculature. (A) Ventral (top panel) and dorsal (bottom panel) gross images show thrombus in internal carotid, middle cerebral, and anterior cerebral arteries and their branches. Black box in ventral view is magnified in (B) top panel. (B) Middle and lower panels show platelet- and fibrin-rich thrombi in cross sections of the ICA. Middle panel is labeled with anti-laminin antibody (red), anti-CD41 platelet antibody (green), and anti-nuclear stain (blue). Bottom panel is labeled with anti-laminin antibody (red), anti-fibrinogen/fibrin antibody (Fbn; green), and anti-nuclear stain (blue). (C) Top panel: triphenyltetrazolium chloride-stained coronal brain section of brain excised 3 h after collagen injection. Black box denotes area from which the images in the two lower panels were taken. Middle panel labeled with anti-laminin antibody (red), anti-CD41 platelet antibody (green), and anti-nuclear stain (blue). Bottom panel labeled with anti-laminin antibody (red), anti-fibrinogen antibody (green), and anti-nuclear stain (blue). Images are representative of six separate experiments. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)