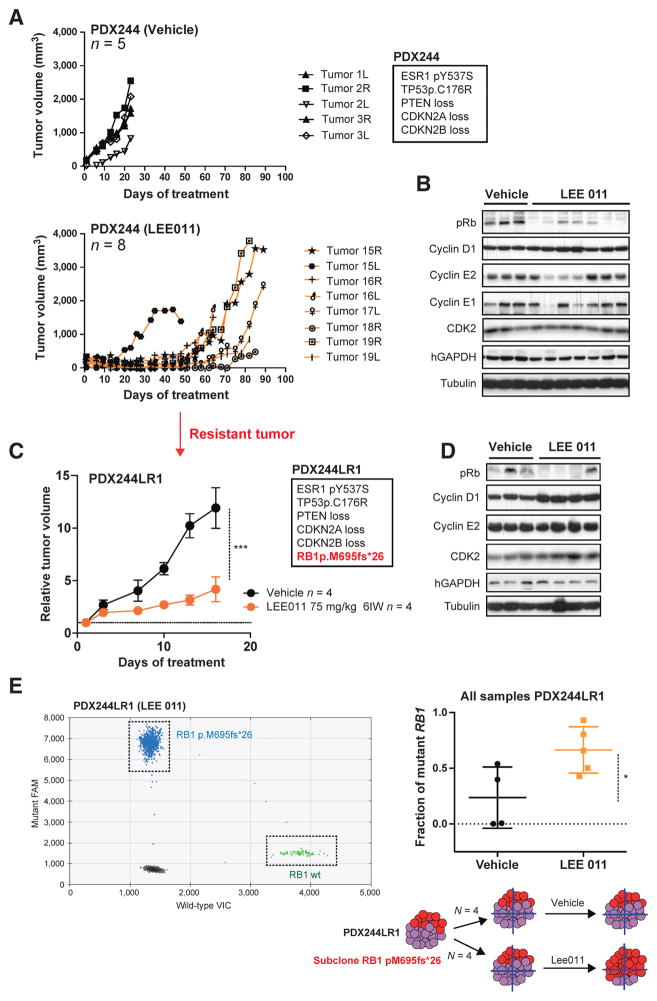
Figure 6.
Acquisition of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition through RB1 mutation in PDX. A, tumor growth of PDX244 following vehicle (top graphic) or LEE011 (75 mg/kg, once daily, 6IW; bottom graphic) treatment. Tumor volume (mm3) is shown over the days of treatment. The total number of mice in each arm (n) and the relevant genetic alterations of PDX244 are indicated. B, Western blots with the indicated antibodies in PDX244 after 23 days of vehicle treatment or 89 days of LEE011 treatment. Each lane belongs to one individual tumor. C, relative tumor growth of PDX244LR1 following vehicle or LEE011 treatment (***, P < 0.001, Student t test). The relevant genetic alterations of PDX244LR1 are indicated. D, Western blots with the indicated antibodies in PDX244LR1 after 16 days of vehicle or LEE011 treatment. Each lane belongs to one individual tumor. E, RB1 pM695fs*26 fraction in vehicle or LEE011-treated samples from PDX244LR1 assessed by ddPCR against RB1 wild-type (*, P < 0.05, Student t test).