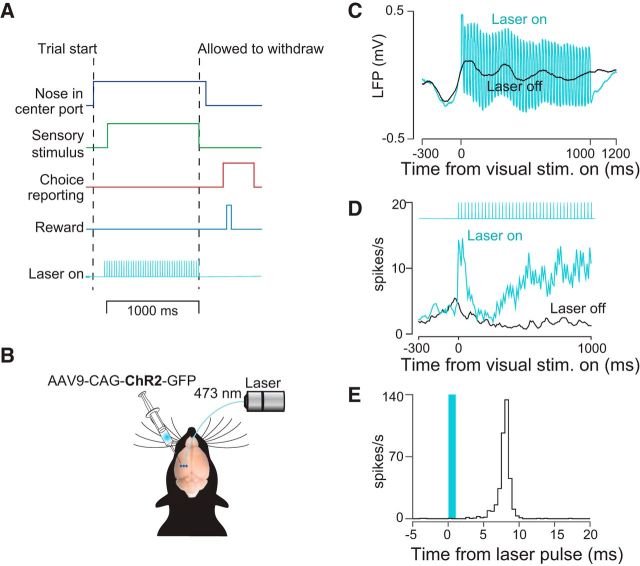
Figure 1.
Decision-making task and strategy for disrupting PPC activity. A, Schematic of decision-making task. Rats initiated trials by inserting their snouts into a port spanned by an infrared beam (dark blue trace). After a variable delay, a series of auditory or visual events began (green trace). Animals were required to remain in a center port for 1000 ms during which time these sensory stimuli were presented. Animals were then allowed to withdraw. They reported choices (red trace) at either a left or right decision port and were rewarded with a drop of water (light blue trace) when correct. Optogenetic stimulation (42 Hz, 5–20 mW, cyan trace) was presented throughout the 1000 ms period on randomly selected trials. B, Schematic of optogenetic approach showing unilateral injections of AAV9-CAG-ChR2-GFP into PPC. C, LFP recorded during laser-on and laser-off trials via a tetrode attached to the stimulating optical fiber. D, Peristimulus time histogram for an example well isolated single neuron for laser-on (cyan) and laser-off (black) trials. E, PETH in which responses are aligned to individual pulses of blue light.