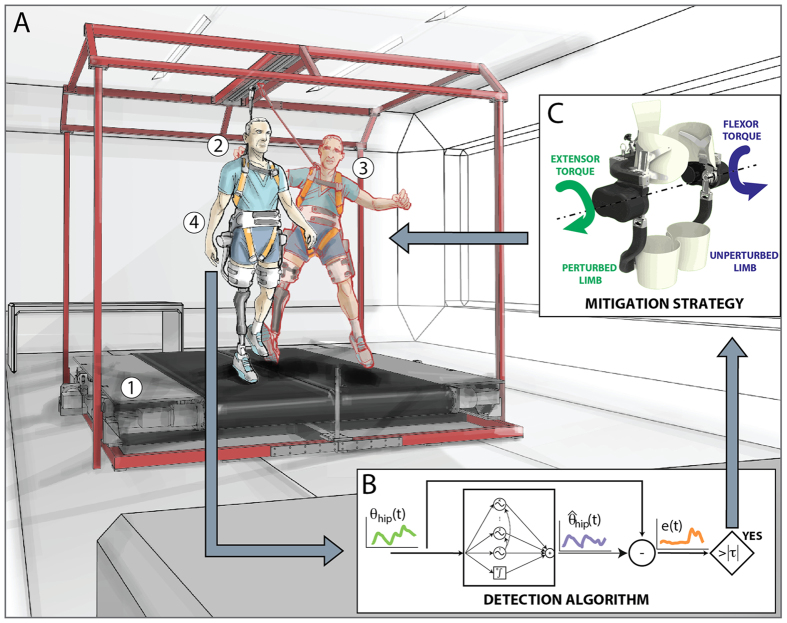
Figure 1. Control strategy.
(A) The mechatronic platform (1) provides sudden and unexpected slipping-like perturbations while the subject was steadily walking (2). The subject’s balance control was hence challenged (3) and, accordingly, the Active Pelvis Orthosis (4) could supply the assistive strategy for stability recovery. (B) The balance loss is detected in real time by an algorithm running in the APO control unit and comparing the actual hip angles of the robot (i.e., θ) with those predicted by a pool of adaptive oscillators (i.e.,  ). (C) Once the slipping-like perturbation was detected, counteracting torques were supplied by the APO at the hip joints to promote balance recovery. Panel C was created by Arch. Alessio Tommasetti Panel C was created by Mr. Francesco Giovacchini.
). (C) Once the slipping-like perturbation was detected, counteracting torques were supplied by the APO at the hip joints to promote balance recovery. Panel C was created by Arch. Alessio Tommasetti Panel C was created by Mr. Francesco Giovacchini.