Table 1. Condition optimization of N-terminal alkylation a , b , c , f .
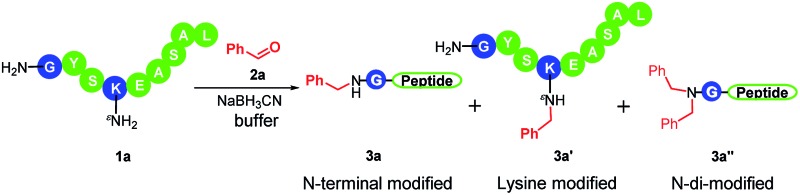
| |||||
| Entry | Buffer | pH | (3a + 3a′) (%) | N-Selectivity d | 3a′′ (%) |
| 1 | A | 3.3 | 49 | >99 : 1 | 38 |
| 2 | B | 4.0 | 58 | 98 : 2 | 30 |
| 3 | A | 6.0 | 60 | 95 : 5 | 22 |
| 4 | B | 6.1 | 78 | >99 : 1 | 18 |
| 5 | C | 7.4 | 60 | 80 : 20 | 20 |
| 6 | D | 9.7 | 35 | 73 : 27 | 7 |
| 7 | C | 10.0 | 50 | 90 : 10 | 10 |
| 8 e | B | 6.1 | 60 | >99 : 1 | 16 |
aThe reaction was performed with 2.7 μmol peptide, 5.4 μmol, benzaldehyde (0.5 M in DMSO), and 13.5 μmol NaBH3CN in 300 μL aqueous solvent at room temperature for 6 h.
bBuffer A is 25 mmol L–1 acetic acid buffer; buffer B is 25 mmol L–1 citric acid buffer; buffer C is 25 mmol L–1 phosphate buffer; buffer D is 25 mmol L–1 borate buffer.
cThe conversion was calculated by area of the corresponding peak under 280 nm UV detection of the reaction system.
dDetermined by MS/MS analysis.
e1.5 equivalents benzaldehyde was used.
fSee ESI Table S1 for more condition screening data.
