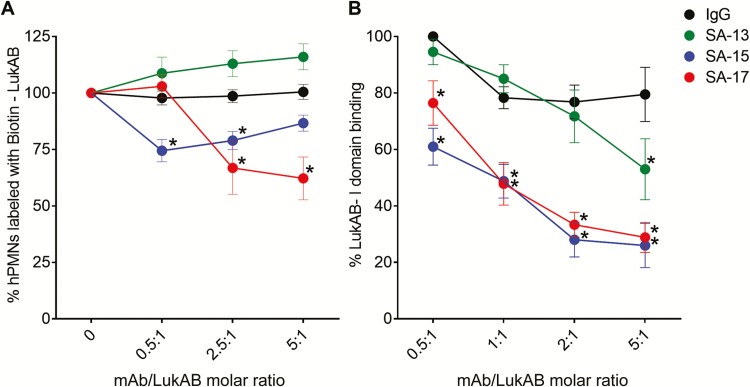
Figure 4.
Monoclonal antibody (mAb)–mediated inhibition of LukAB binding. A, LukAB binding to hPMN surface. Dilutions of mAbs were preincubated with a fixed concentration of Biotin–LukAB (5 µg/mL) to give indicated molar ratios. LukAB–mAb mixture was added to hPMNs (n = 4 donors) on ice for 10 minutes before cell washing, staining, and FACS analysis. Inhibition of Biotin–LukAB binding to cell surface by SA-15 and SA-17 indicate that these antibodies are blocking the receptor binding site of the toxin. B, Monoclonal antibody–mediated inhibition of LukAB binding to CD11b I-domain. LukAB was added to wells coated with purified human CD11b-I domain in presence or absence of mAbs, and residual LukAB binding was determined. Mean ± SEM are plotted. For B, n = 4 independent experiments. *P < .05 using 2-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s post hoc test correction for multiple comparisons. Each mean was compared with immunoglobulin G control for statistical analysis. Abbreviations: FACS, fluorescence activated cell sorting; hPMNs, human polymorphonuclear neutrophils; IgG, immunoglobulin G; mAb, monoclonal antibody.