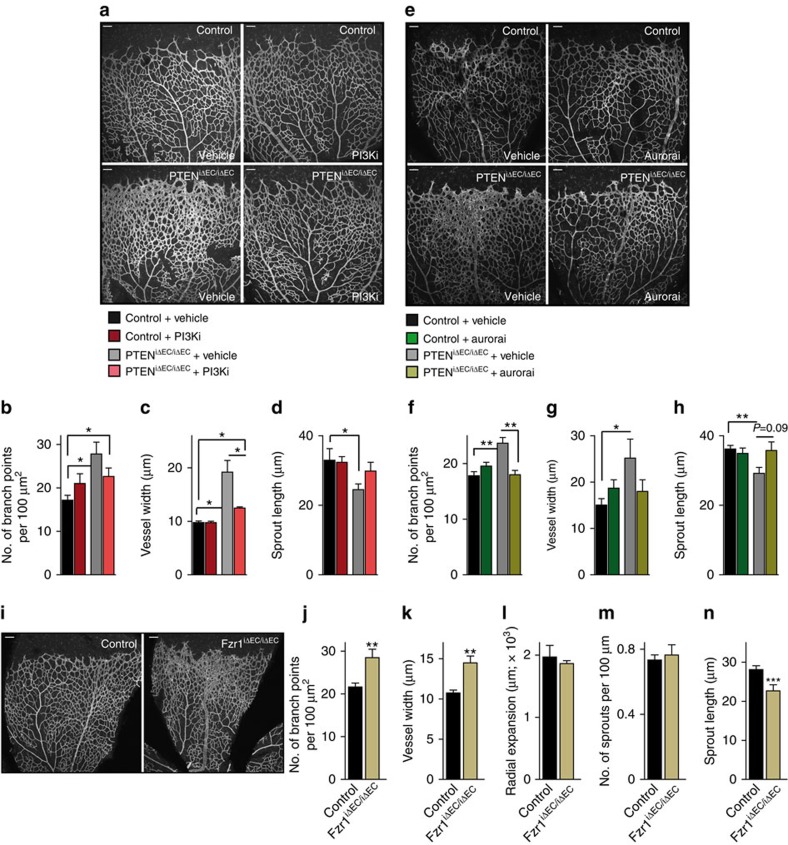
Figure 6. Dual function of PTEN in sprouting angiogenesis.
(a) IB4-stained control and PTENiΔEC/iΔEC P7 retinas (4-OHT administration from P1 to P2) treated with vehicle or GDC-0941 at P6 and P7. (b–d) Quantitative analysis of the retinas shown in a. (b) Vascular branch points per unit area (n≥4). (c) Vessel width (n≥4). (d) Sprout length from the tip to the base of the sprout (n≥4). (e) IB4-stained control and PTENiΔEC/iΔEC P7 retinas (4-OHT administration from P1 to P2) treated with vehicle or VX680 at P6 and P7. (f–h) Quantitative analysis of the retinas shown in e. (f) Vascular branch points per unit area (n≥6). (g) Vessel width (n≥6). (h) Sprout length from the tip to the base of the sprout (n≥6). (i) Overview of P7 control and Fzr1iΔEC/iΔEC iB4-stained. (j–n) Quantitative analysis of the retinas shown in i. (j) Vascular branch points per unit area (n=11). (k) Vessel width (n=11). (l) Radial expansion of blood vessels (n≥5). (m) Number of sprouts per vascular front length (n=11). (n) Sprout length from the tip to the base of the sprout (n=6). Scale bars, 100 μm (a,e,i). Error bars are s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 were considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed by nonparametric Mann–Whitney test.