Figure 6. Physiological-relevant changes in glucose concentrations enhance MSH-induced CRE-dependent reporter activation.
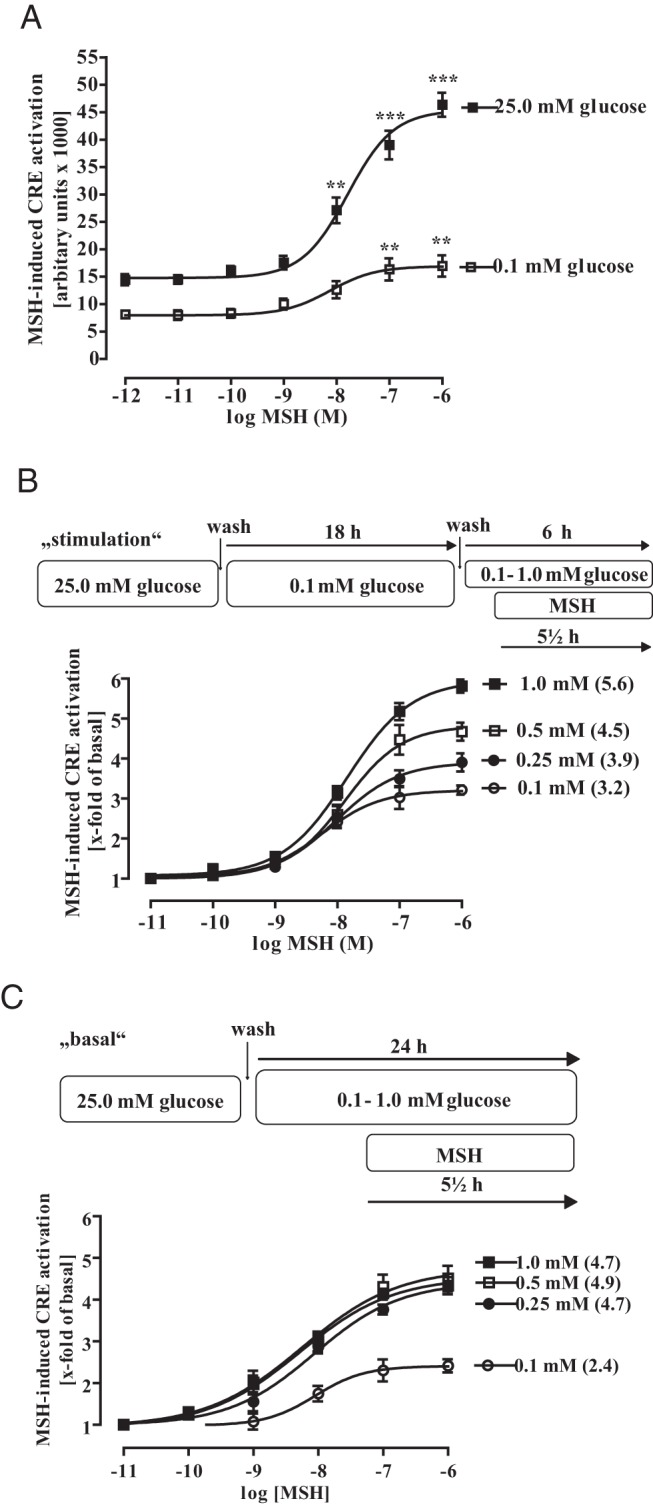
A, mHypoA-2/12-CRE cells were either cultured with 25.0mM or 0.1mM glucose for 18 and then stimulated with various MSH concentrations for additional 6 hours without changing the glucose level. Data of 5 independent experiments performed in quadruplicates were compiled, expressed as the mean ± SEM, and fitted to dose-response curves with fixed slopes. Asterisks indicate a significant difference to the basal values obtained with no MSH. B, Cells were cultured for 18 hours with 0.1mM glucose and then with 0.1mM, 0.25mM, 0.5mM, or 1.0mM glucose (as indicated) for additional 6 hours to obtain basal CRE activity. To measure MSH-induced CRE-dependent reporter activation distinct pools of cells were also stimulated with the indicated MSH concentration for the last 5.5 hours without changing the glucose level. Data of 5 independent experiments performed in quadruplicates were compiled, by calculating the corresponding x-fold of basal value, expressed as the mean ± SEM, and fitted to dose-response curves with fixed slopes. Numbers in parenthesis indicate the x-fold over basal for 1.0μM MSH. C, Cells were cultured with 0.1mM, 0.25mM, 0.5mM, or 1.0mM glucose (as indicated) for 24 hours to obtain basal CRE activity. To measure MSH-induced CRE-dependent reporter activation, distinct pools of cells were stimulated or not with the indicated MSH concentrations for the last 5.5 hours without changing the glucose concentration. Data of 5 independent experiments performed in quadruplicates were compiled, by calculating the corresponding x-fold of basal value, expressed as the mean ± SEM, and fitted to dose-response curves with fixed slopes. Numbers in parenthesis indicate the x-fold over basal for 1.0μM MSH.
