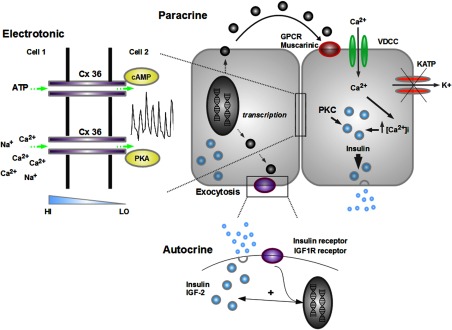
Figure 2.
Schematic depicting cell-cell signaling modalities present within human islets. Chemical messengers act on the cell of origin (autocrine) or close neighbors (paracrine), and increase both insulin transcription and secretion. GJs composed of Cx36 provide electrotonic coupling between adjacent cells and also facilitate passage of small molecular weight molecules such as adenine nucleotides along their diffusion gradients (shown in blue). GJ transcription, phosphorylation status, and function can all be modulated by a range of intracellular signals including protein kinase A (PKA) and cAMP (figure adapted from Ref. 57). HI, high; KATP, ATP-sensitive K+ channel; LO, low; PKC, protein kinase C; VDCC, voltage-dependent calcium channel.