Figure 3.
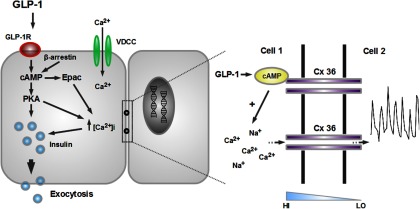
Incretins evoke coordinated activity in a subnetwork of human β-cells to influence insulin release. At permissive glucose concentrations, GLP-1 binding to the GLP-1R leads to stimulation of adenylate cyclase activity and generation of cAMP, as well as engagement of a β-arrestin scaffold. By interacting with downstream partners such as exchange protein activated by cAMP (Epac) and protein kinase A (PKA), GLP-1 potentiates insulin release via effects on Ca2+-influx and Ca2+-sensitivity of exocytosis. Coordinated intercellular transmission of GLP-1-derived signals is achieved by GJ coupling, and GLP-1 may modulate this in a state-dependent manner via its cAMP-raising effects (blue ramp; diffusion gradient) (figure adapted from Ref. 57). GLP-1R, GLP-1 receptor; HI, high; LO, low.