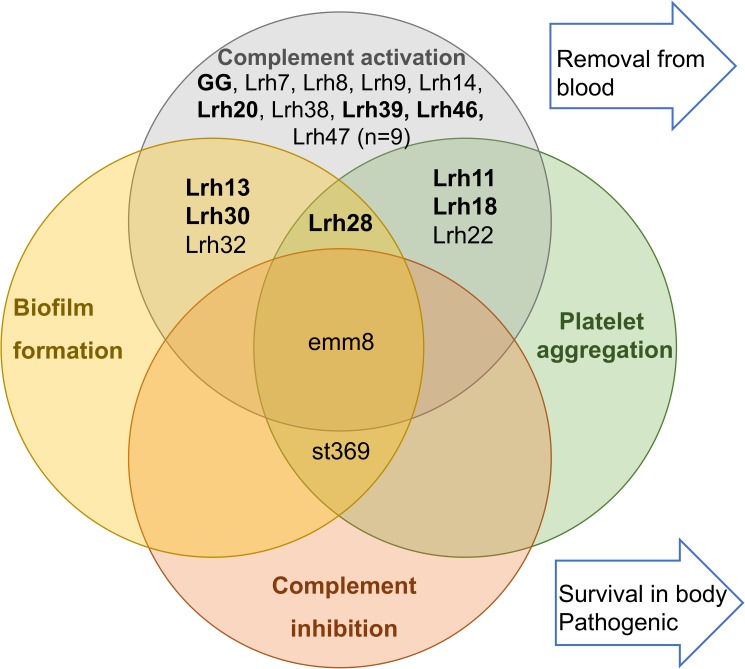
Fig 4. Immunological properties of L. rhamnosus GG, clinical isolates and pathogens towards the human host based on in vitro data.
Strains Lrh7, Lrh8, Lrh9, Lrh14, Lrh20, Lrh46, Lrh47, Lrh38 and Lrh39 displayed comparable properties as observed in L. rhamnosus GG. All these strains activate the complement in serum. Strains Lrh13, Lrh30 and Lrh32 also induced more biofilm formation more than GG. Strains Lrh11, Lrh18 and Lrh22 were aggregating with platelets. Strain Lrh28 was doing both causing platelet aggregation and biofilm formation. The pathogenic group A Streptococcus strain emm8 induced complement activation, but it could bind complement regulator C4bp to evade complement. The pathogenic strain st369 could bind complement regulators C4bp and factor H and did not induce complement activation. A similar type of GAS strain has been shown to cause platelet aggregation [36] and biofilm formation [37]. The bolded strains have SpaCBA pili similar to GG.