Fig 3. Fructooligosaccharides (FOS) or dead L. salivarius feeding reduced enteric bacteria as well as K. pneumoniae translocation to liver and increased hepatic bacteria clearance in STZ-DM mice.
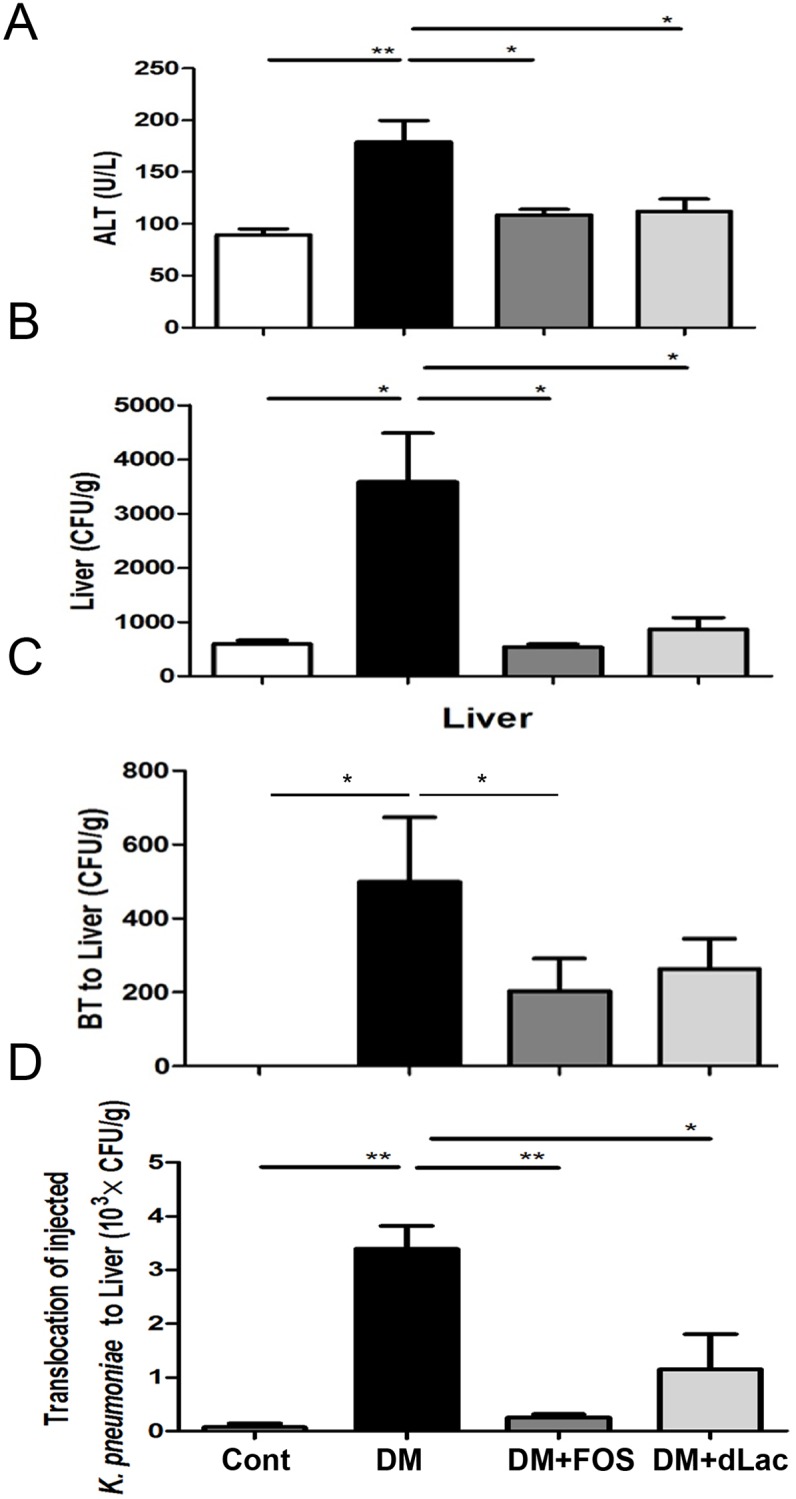
(A) The level of serum ALT was significantly increased in STZ-DM mice. FOS and dead L. salivarius supplementation significantly decreased serum ALT levels in STZ-DM mice. (B) STZ-DM mice demonstrated a significant increase of K. pneumoniae loads of liver after injection of K. pneumoniae in the superior mesenteric vein as compared with that in the control group. FOS or dead L. salivarius feeding significantly decreased the bacterial loads of liver in STZ-DM mice. (C) FOS or dead L. salivarius feeding decreased diabetes-induced bacterial translocation to liver in STZ-DM mice. (D) FOS or dead L. salivarius feeding significantly decreased diabetes-induced pathogenic K. pneumoniae translocation to liver in STZ-DM mice. K. pneumoniae (5 × 107 CFU in 500 μl of normal saline) was injected into the isolated intestinal segment. After 2 h, liver was collected, weighed, and homogenized in equal volume of sterile saline for culture. ALT, alanine transaminase; BT, bacterial translocation; STZ, streptozotocin; DM, diabetes mellitus; FOS, fructooligosaccharides; dLac, dead L. salivarius. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. n = 6/group.
