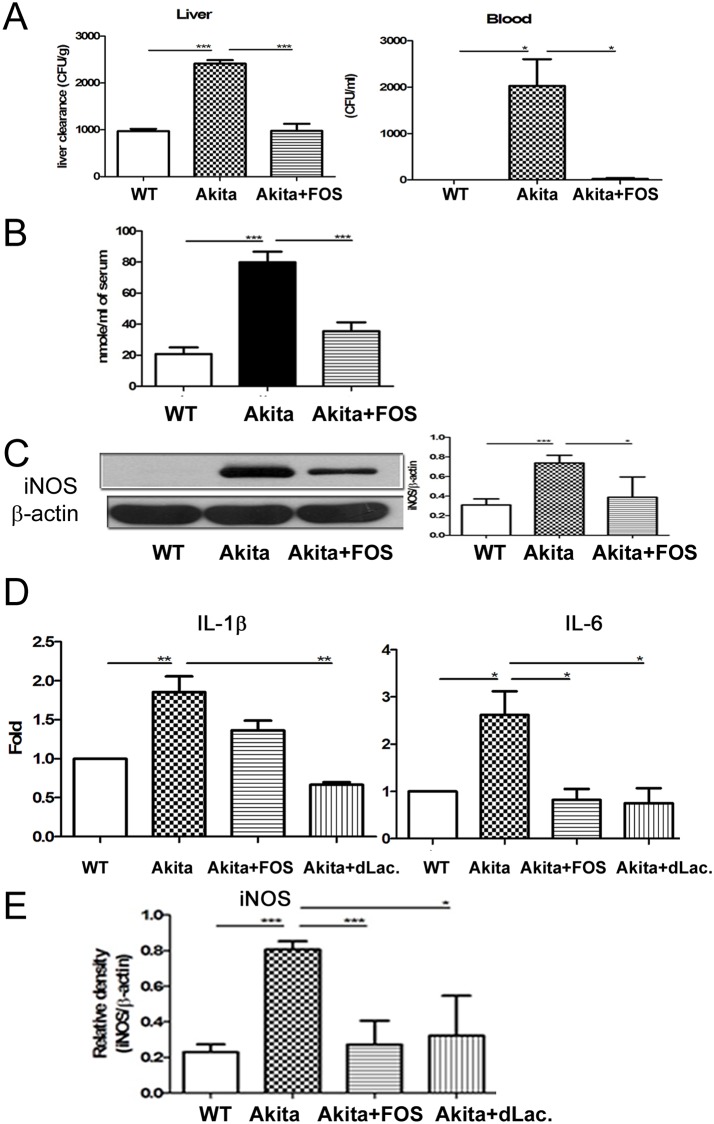
Fig 6. FOS feeding reversed diabetes-induced hepatic bacterial clearance impairment, IL-1β expression of the Kupffer, and iNOS expression of the intestinal mucosa in Ins2Akita mice.
(A) Ins2Akita mice demonstrated a significant increase of K. pneumoniae translocation to liver and blood as compared with that in WT group. FOS supplementation significantly increased hepatic bacteria clearance and decreased K. pneumonia translocation to liver as well as blood in Ins2Akita mice. K. pneumoniae (1 × 103 CFU, K2 serotype) were injected into the branch of superior mesenteric vein (SVC). The liver was collected, weighed and homogenized in 1 ml of sterile saline at 4 hr after the injection. 100 μl of blood were taken from heart. Blood or aliquots of the homogenates were plated onto tryptic soy broth (TSB) agar plates (DIFCO). (B) Diabetes induced plasma NO levels in the portal vein as measured by Griess reagents and FOS feeding decreased them. (C) Diabetes significantly induced iNOS protein expression of the intestinal mucosa in Ins2Akita mice and FOS feeding decreased it. (D) Diabetes induces a significant increase of IL-1β as well as IL6 expression of Kupffer cells in Ins2Akita mice. FOS or dead L. salivarius supplementation markedly decreased it. (E) Diabetes induced iNOS mRNA expression of the intestinal mucosa in Ins2Akita mice. FOS or dead L. salivarius supplementation decreased it. STZ, streptozotocin; DM, diabetes mellitus; FOS, fructooligosaccharides; dLac, dead L. salivarius. *, P< 0.05; **, P< 0.01; ***, < 0.001. n = 6/group.