Figure 7. Fumarate and Glyoxylate Manipulate Tobramycin Sensitivity in Clinically Relevant Models of P. aeruginosa Infection.
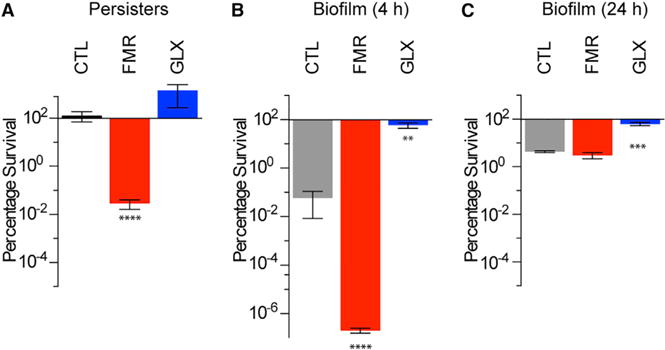
(A) Survival of ciprofloxacin persister cells following 4 hr treatment with 40 mg/L tobramycin and supplementation with no carbon metabolite (CTL), 15 mM fumarate (FMR), or 30 mM glyoxylate (GLX). (B and C) Survival of young (4 hr) (B) and mature (24 hr) (C) colony-forming biofilms treated for 24 hr on LB agar with 8 mg/L tobramycin and supplementation with no carbon metabolite (CTL), 15 mM fumarate (FMR), or 30 mM glyoxylate (GLX).
Values in all bar graphs depict the mean ± SEM with significance reported as FDR-corrected p values in comparison with untreated control (CTL): **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001 (n = 3).
