Fig. 1.
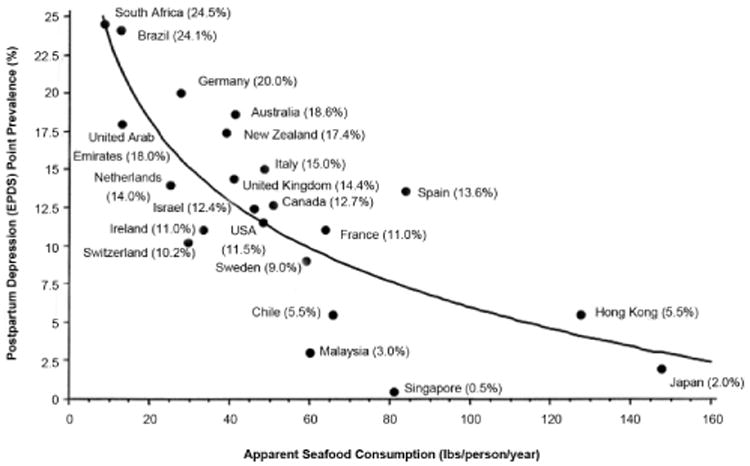
Cross-national rates of postpartum depression as a function of seafood consumption. The graph shows the inverse correlation between apparent seafood consumption (in pounds per person, per year; calculated by adding the country's yearly seafood catch and imports minus its exports) and prevalence of postpartum depression by country. This association remained significant after adjusting for gross domestic product and after removing outlying Asian nations. EPDS = Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale. Reprinted from “Seafood Consumption, the DHA Content of Mothers' Milk and Prevalence Rates of Postpartum Depression: A Cross-National, Ecological Analysis,” by J. R. Hibbeln, 2002, Journal of Affective Disorders, 69, p. 22 Copyright 2002 by Elsevier. Reprinted with permission.
