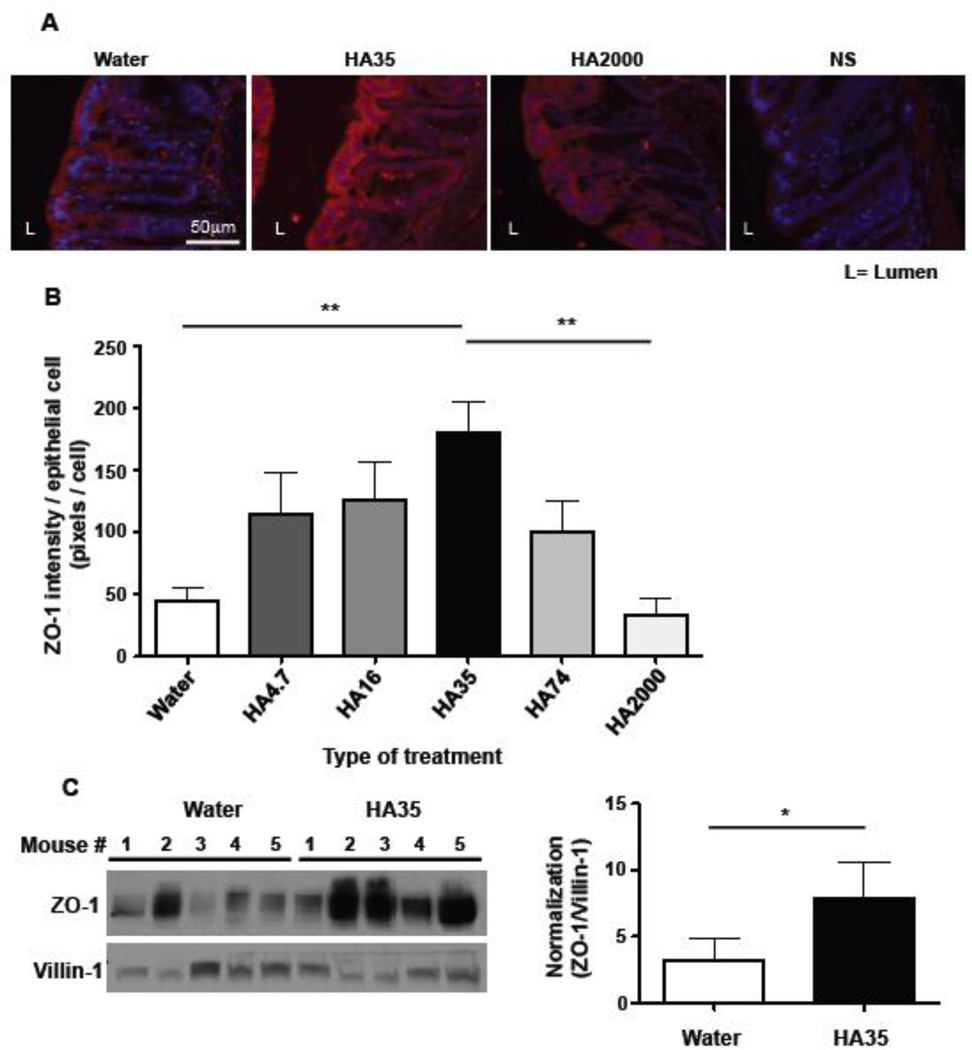
Figure 2. Oral delivery of low molecular weight HA to healthy mice increases ZO-1 expression in the distal colon in a size dependent manner.
A. Sections of distal colon from wild type mice gavaged once daily with water or 300µg of multiple sizes of hyaluronan (HA) (4.7, 16, 35, 74, and 2000 kDa) for three days were immunostained for ZO-1 (red) and nuclei were stained blue (DAPI). Representative fluorescent micrographs show ZO-1 staining in the colonic epithelium of distal colons of mice treated with water or with HA35 or with HA2000. Non-specific (NS) indicates the secondary antibody staining control. B. Images were quantified using 3 stained sections per mouse and 3 mice per group. ZO-1 staining intensity was measured as described in “Methods” and normalized to the number of epithelial cells by counting the number of epithelial cell nuclei. One-way ANOVA was used to test the significance of the differences between various sizes of HA-treated groups and water-treated group. (**, p<0.01). C. Western blot analysis of ZO-1 protein in distal colon tissue lysates from water- or HA35-treated wild type mice (300µg/mouse, once daily for 5 days). The same volume of each lysate was loaded per lane and the levels of ZO-1 were normalized to the expression levels of villin-1 (an epithelial cell marker). The densitometric quantification of ZO-1 and villin-1 protein bands was used to calculate the relative expression level of ZO-1 in epithelium of water and HA35-treated mice (5 mice per group). The one-tailed Mann-Whitney test was used to test the significance of difference between groups, and a significant difference is indicated in the figure (*, p<0.05). Error bars=S.E.M.