Figure 1.
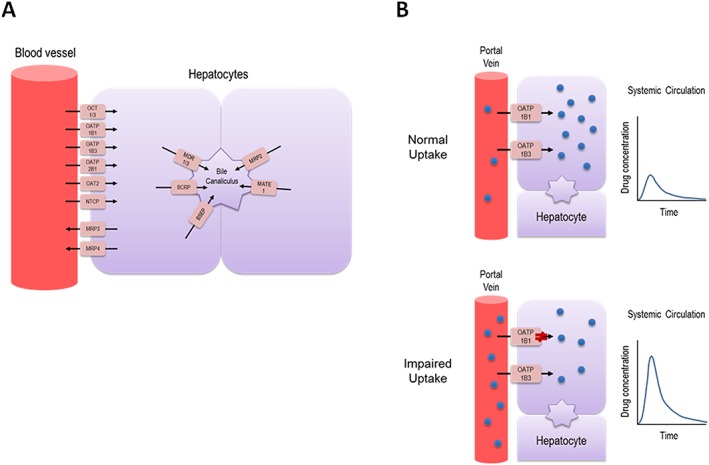
Summary of transporters expressed in human hepatocytes involved in mediating drug uptake and efflux (A), and illustration of the impact of SLCO1B1 genetic variation on drug disposition in vivo (B). Individuals carrying a dysfunctional genetic variant in SLCO1B1 results in impaired hepatocellular uptake of drug substrates as compared to wild type individuals, leading to significantly increased plasma exposure, which may increase risk for drug‐induced adverse effectsBCRP, breast cancer resistance protein; BSEP, bile salt export pump; MATE, multidrug and toxin extrusion; MDR, multidrug resistance protein; MRP, multidrug resistance‐associated protein; NTCP, sodium/taurocholate co‐transporting polypeptide; OAT, organic anion transporter; OATP, organic anion transporting polypeptide; OCT, organic cation transporter
