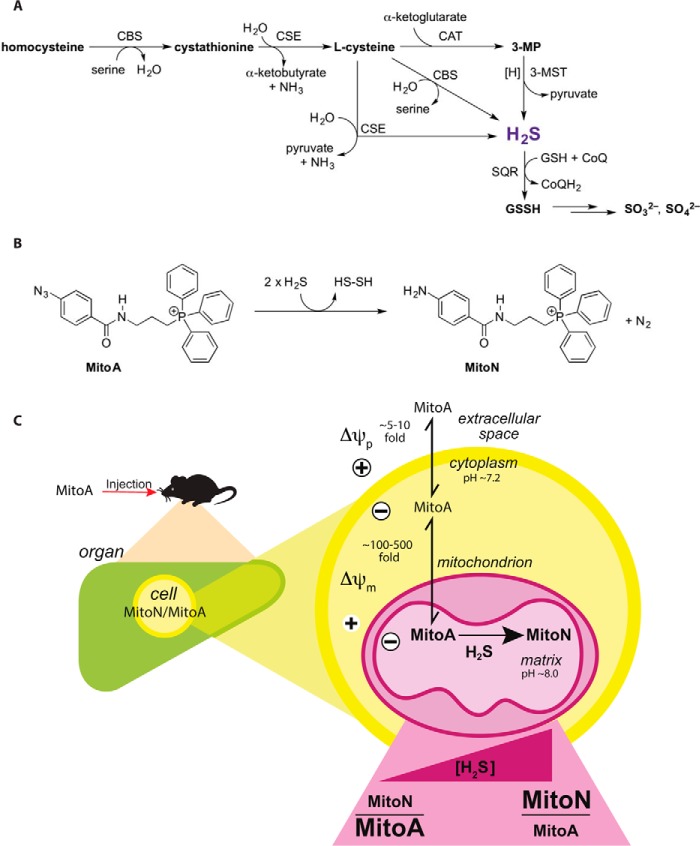
Figure 1.
Overview of endogenous H2S production and rationale for its detection by MitoA. A, overview of H2S metabolism (sulfur-containing compounds in bold). CBS, cystathionine β-synthase; CSE, cystathionine β-lyase; CAT, cysteine aminotransferase; GSSH, glutathione persulfide; 3-MP, 3-mercaptopyruvate; 3-MST, 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase. B, reaction of MitoA with H2S to form MitoN. C, model of uptake of MitoA into mitochondria in vivo, followed by its conversion to MitoN upon reaction with H2S. The subsequent extraction of MitoA and MitoN from the tissue and analysis by LC-MS/MS enables changes in the levels of H2S in vivo to be inferred.