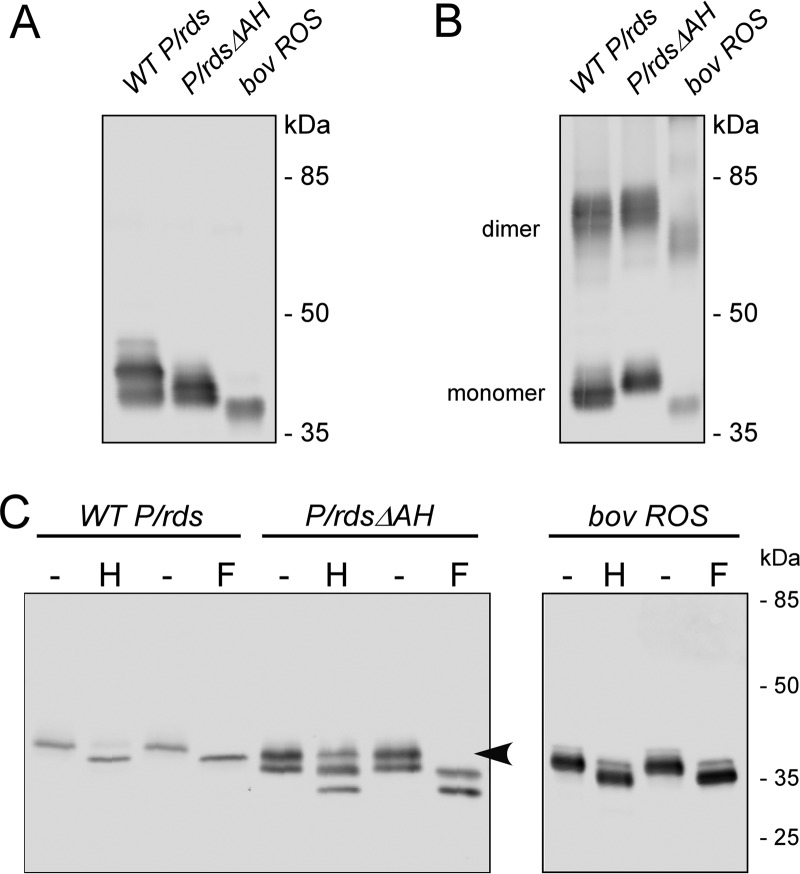
Figure 2.
Deletion of the P/rds C-terminal AH does not impair protein biosynthesis or disulfide-mediated dimerization. A and B, stably expressing HEK AD293 cells were treated with N-ethylmaleimide to block free thiols, and Triton X-100 extracts were subjected to non-reducing (A) and reducing (B) 10% SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting analysis with anti-P/rds monoclonal antibody MabC6. An extract from bovine rod OSs was analyzed in parallel for comparison. These data indicate that deletion of the C-terminal AH does not affect disulfide-mediated P/rds dimerization. C, post-translational carbohydrate modifications were analyzed using PNGase F (F) and Endo H (H) glycosidases, which cleave glycoprotein oligosaccharides. The former removes almost all types of N-linked glycosylation, but resistance to the latter is a signature of Golgi processing. WT P/rds expressed in cultured cells shows greater heterogeneity in glycosylation than does the native protein from rod OS membranes (27).