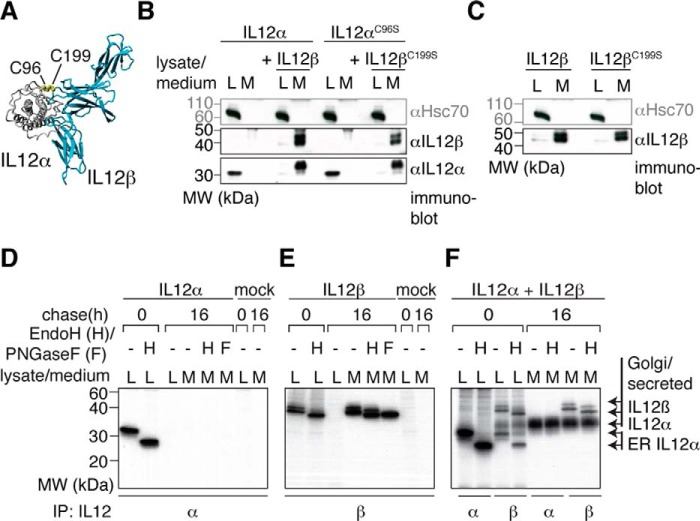
Figure 1.
IL-12α secretion depends on IL-12β co-expression. A, IL-12 structure. IL-12 is composed of two covalently linked subunits (IL-12α and IL-12β, structure based on PDB code 3HMX). The IL-12α subunit is depicted in gray and the IL-12β subunit in blue. The intermolecular disulfide bond between IL-12α Cys-96 and IL-12β Cys-199 is shown in a yellow CPK representation. B, IL-12α secretion analyzed by immunoblotting. IL-12α is retained in the cell when expressed in isolation (L, lysate), and co-expression of IL-12β induces its secretion (M, medium) independent of the presence or absence of the cysteine residues that form the IL-12α-IL-12β disulfide bridge. 1% lysate or medium was applied to the gel and blotted with the indicated antibodies. Hsc70 served as a loading control. MW, molecular weight. C, IL-12β secretion analyzed by immunoblotting. The same as in B, except isolated IL-12β and its C199S mutant were analyzed. D, IL-12α secretion and glycan modification by metabolic labeling. Cells were transfected with IL-12α or empty pSVL vector (mock) and metabolically labeled for 1 h before they were chased for the indicated times. Immunoprecipitations (IP) from cell lysates or media were performed with IL-12α antibodies and samples were treated with Endo H (H) or PNGase F (F) where indicated. E, IL-12β secretion and glycan modification by metabolic labeling. The same as in D, except IL-12β was analyzed. F, IL-12 secretion and glycan modification upon co-expression of IL-12α and IL-12β by metabolic labeling. The same as in D, except IL-12α was co-transfected with IL-12β.