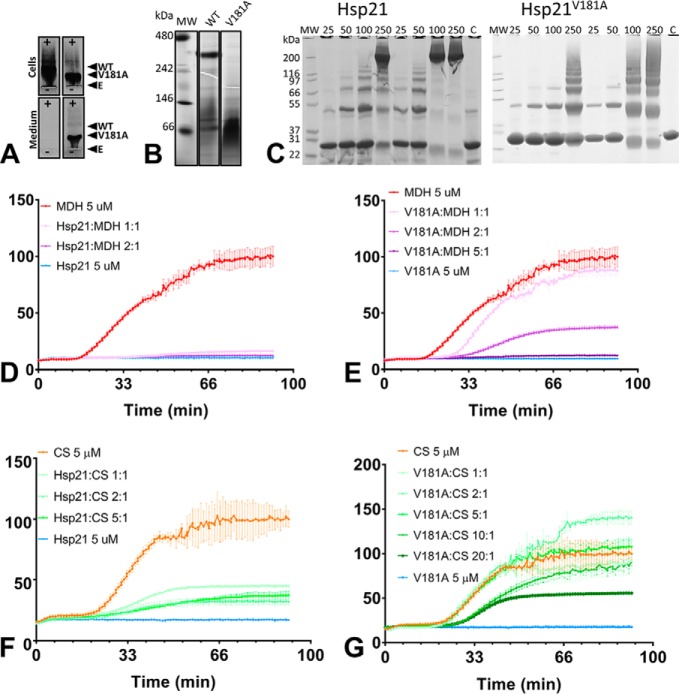
Figure 7.
The V181A mutational variant of Hsp21 is non-dodecameric and has decreased chaperone activity. A, non-denaturing agarose gel electrophoresis. Panels show aliquots withdrawn from cells and medium before harvesting the cells; in each panel pair there is Hsp21 (left) and Hsp21V181A (right). Labels indicate the positions of Hsp21 (WT) and Hsp21V181A (V181A) and the entry point for loading (E). The image shows the overexpressed proteins as they migrate toward the anode (+) and that, already before purification, the mutational variant Hsp21V181A is of smaller size compared with Hsp21 and that Hsp21V181A leaks out into the medium. C, denaturing SDS-PAGE of Hsp21 WT and Hsp21V181A mutational variant cross-linked with lysine-specific cross-linker at various protein concentrations (25–250 μm) at protein/cross-linker ratios of 1:10 and 1:60. C, control samples without cross-linker. A protein concentration of 250 μm Hsp21 corresponds to ∼5 mg/ml (calculated based on monomeric mass 21 kDa). D, chaperone activity of Hsp21, determined as its suppression of heat-induced aggregation of the model substrate protein MDH at molar ratios of 1:1 and 2:1. E, chaperone activity of Hsp21V181A mutational variant, determined as its suppression of heat-induced aggregation of the model substrate protein MDH at molar ratios of 1:1, 2:1, and 5:1. F, chaperone activity of Hsp21, determined as its suppression of heat-induced aggregation of the model substrate protein CS at molar ratios of 1:1, 2:1, and 5:1. G, chaperone activity of Hsp21V181A mutational variant, determined as its suppression of heat-induced aggregation of the model substrate protein CS at molar ratios of 1:1, 2:1, 5:1, 10:1, and 20:1.