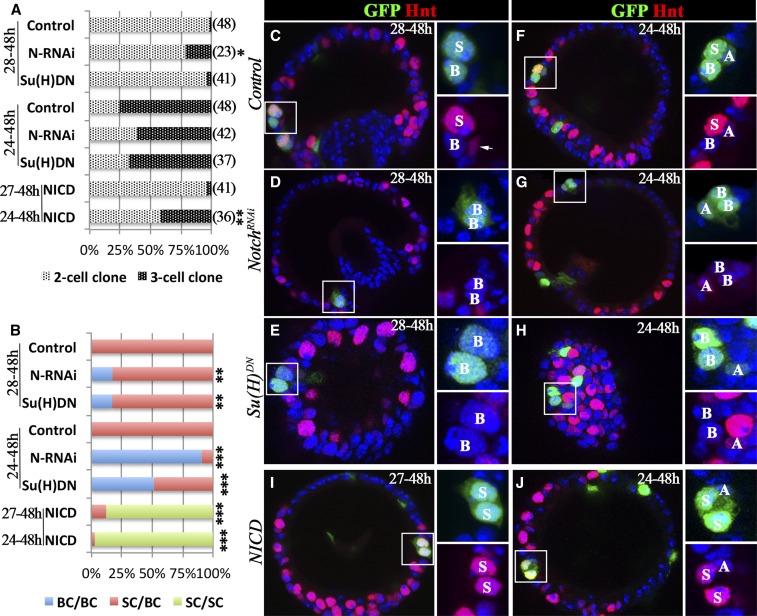
Figure 4.
Notch signaling is required and sufficient for SC fate. Flip-out clones are marked by GFP expression (green in C–J), and Hnt expression is shown in red (C–J). (A and B) Quantification of SC-clone distribution according to clone size (A) or clone composition (B) when induced at multiple time points. The number of clones analyzed is shown in parentheses. The category in (B) only indicates the BC and SC, regardless of whether or not the clone contains the AC. Fisher’s exact test was used for assessing statistical significance (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001). (C–E) Representative spermathecae with control (C), N-knockdown (D), or Su(H)DN-overexpressing (E) clones induced at 28 hr and observed at 48 hr APF (28–48 hr). The square areas are showed at higher magnification with only two channels in the right two subpanels. The clone cell identity is marked by A, B, or S for AC, BC, or SC, respectively. The arrow in (C) points to an AC with elongated nuclei and faint Hnt expression, which is not in the clone. (F–H) Representative spermathecae with control (F), N-knockdown (G), or Su(H)DN-overexpressing (H) clones induced at 24 hr and observed at 48 hr APF (24–48 hr). (I–J) Representative spermathecae with NICD-overexpressing clones induced at 27 (I) and 24 hr (J), and observed at 48 hr APF (27–48 and 24–48 hr, respectively). AC, apical cell; APF, after puparium formation; BC, basal cell; DN, dominant negative; GFP, green fluorescent protein; Hnt, Hindsight; N, Notch; NICD, Notch intracellular domain; RNAi, RNA interference; SC, secretory cell; Su(H), Suppressor of Hairless.