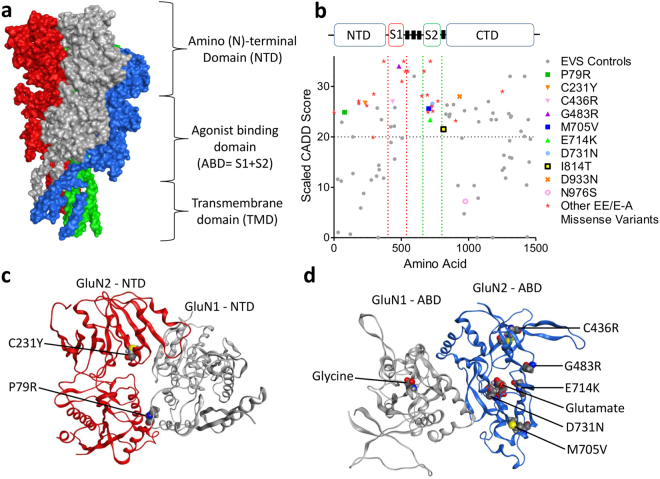
Figure 1.
CADD scores and protein modelling predict stronger functional effects for EAS-associated GRIN2A mutations than in controls. (a) Protein structure model of NMDAR (PDB ID 4TLL): GluN1 (grey and green), GluN2 (B in this structure) (blue and red). Membrane would be horizontal in this image with the NTD and ABD in the extracellular space. Intracellular C-Terminal domain would be below the transmembrane domain (not present in this structure). (b) Schematic linear representation of GluN2A with the domains annotated. Black rectangles indicate transmembrane domains. Plot of scaled CADD scores against GluN2A amino acid position for missense variants. Black dots represent scores for 65/6474 individuals from the Exome Variant Server (EVS) that had missense variants in GRIN2A and coloured symbols are scores for variants found in individuals with EAS disorders. The horizontal dotted line indicates the scaled CADD score cut off of 20 for a highly likely deleterious variant. (c) Protein structure model of the NTD of NMDAR (PDB ID 3QEL): GluN1 (grey), GluN2 (B in this structure) (red). Mutations considered in this domain highlighted (conserved between GluN2A and B). (d) Protein structure model of the LBD of NMDAR (PDB ID 2A5T): GluN1 (grey), GluN2A (blue). Mutations considered in this paper highlighted, as well as agonists.