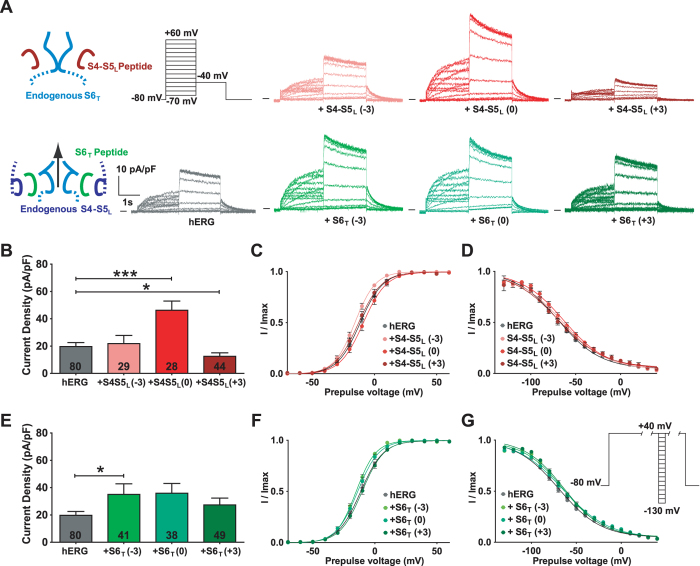
Figure 2.
S4-S5L (+3) peptide inhibits and S6T (−3) peptide activates hERG channels. (A) Representative, superimposed recordings of the WT hERG current in the absence (0.6 µg hERG plus 1.4 µg GFP plasmids) and in the presence of S4-S5L or S6T peptides (0.6 µg hERG plus 1.4 µg peptide plasmids). Left: schemes of the hypothetical effects of S4-S5L inhibiting or S6T activating peptide; activation voltage protocol used (one sweep every 8 s) located above the WT hERG currents; right: data from experiments performed in the presence of various S4-S5L or S6T peptides. (B) Mean hERG tail-current density at −40 mV after a prepulse at +60 mV in the presence of S4-S5L peptides. (C) Activation curve, obtained from tail currents using the protocol shown in A, in the presence of S4-S5L peptides (n = 21–65). (D) Inactivation curve in the presence of S4-S5L peptides (n = 6–24). Inset, Inactivation voltage protocol used (one sweep every 5 s, first pulse = 1 s, second pulse = 15 ms, third pulse = 0.5 s). (E) Through (G) same as B through D, in the presence of S6T peptides (F, n = 28–65; G, n = 15–24). *p < 0.1, ***p < 0.01 versus control hERG, Mann-Whitney test.