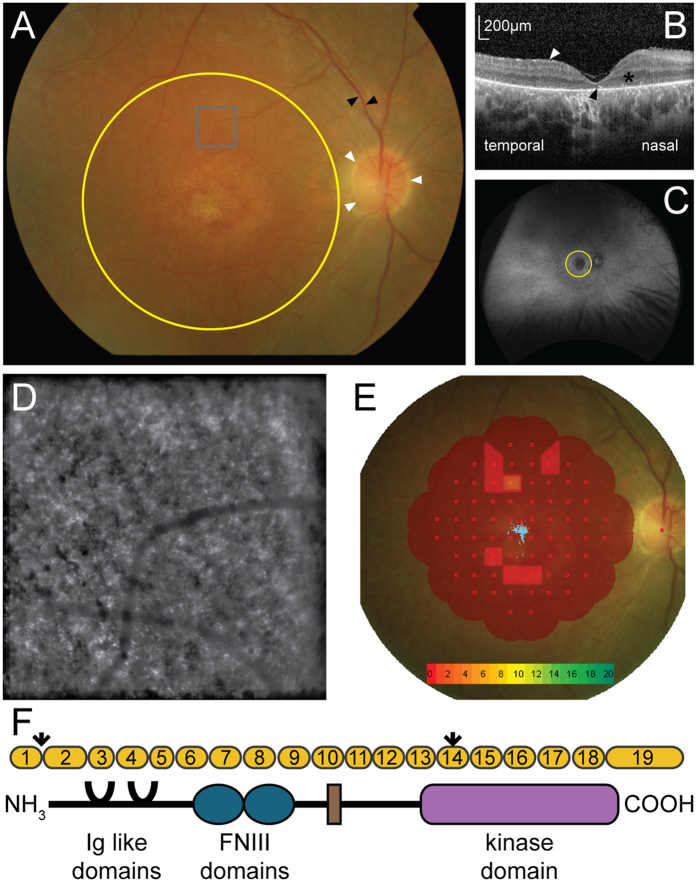
Figure 1.
Phenotypic characterisation of an individual with MERTK associated retinal dystrophy. (A) Fundus photo of the right eye showing the optic nerve (white arrows), retinal vessels (black arrows) and macula area (yellow circle). (B) Optical coherence tomography at the right fovea showing epiretinal fibrosis (white arrow), the outernuclear layer (*) and expected position of the ellipsoid layer (black arrow). (C) Widefield Optos autofluorescence image of the right retina showing the macula (yellow circle) and peripheral retina. (D) ImagineEyes adaptive optics image of the right retina at 5 degrees superior to the fovea (grey box on panel A). (E) Interpolated map of Nidek microperimetry of the right macula, with decibel scale (collection of blue points in centre of macula = fixation). (F) Schematic of MERTK gene displaying the exons (yellow), the two variants (arrows), one in the first base of intron 1, predicted to interfere with splicing and a premature stop in exon 14, and the protein domains of MERTK.