Figure 5.
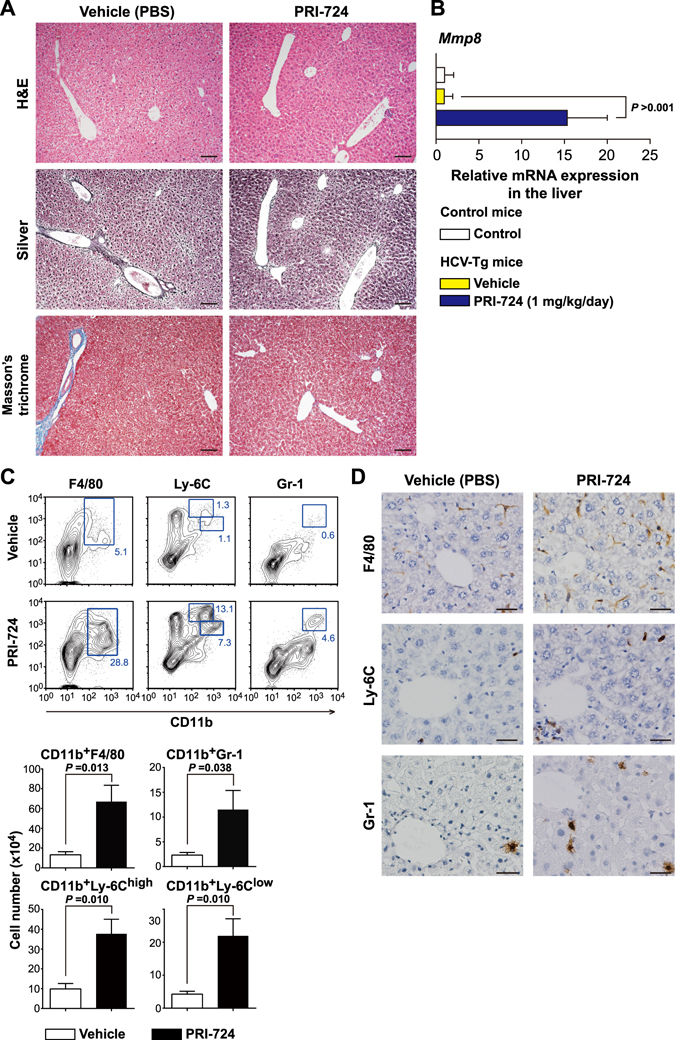
Subcutaneous continuous administration of PRI-724 is effective for treating fibrosis induced by HCV. HCV transgenic mice were treated with PRI-724 (1 mg/kg body weight) or vehicle (PBS) by continuous subcutaneous infusion for six weeks. Undosed non-transgenic mice were used as controls. (A) Liver damage and fibrosis were assessed by staining with hematoxylin and eosin (upper panels), silver stain (middle panels), and Masson’s trichrome (lower panels). Representative images are provided (scale bars = 100 μm). (B) The liver expression of Mmp8 mRNA in non-transgenic control mice (white) and HCV transgenic mice treated with vehicle (yellow) or with PRI-724 (blue) was determined by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. (C) Representative scatter plots of each cell subset are shown in left panels. The absolute numbers of F4/80+CD11b+ (macrophages), Ly-6C++CD11b+ and Ly-6C+CD11b+ (monocytes), and Gr-1+CD11b+ cells (neutrophils) in intrahepatic leukocytes were determined by FACS (right panels). (D) Expression of F4/80, Ly-6C, and Gr-1 was examined by immunohistochemistry with anti-F4/80, -Ly-6C, and -Gr-1 antibodies. Representative images are provided (scale bars = 100 μm). Data are shown as the mean ± SD (control: n = 6; vehicle: n = 4; PRI-724 (1 mg/kg, daily): n = 4). Significance was assessed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test as indicated; significant relationships are indicated by P-values.
