Figure 4.
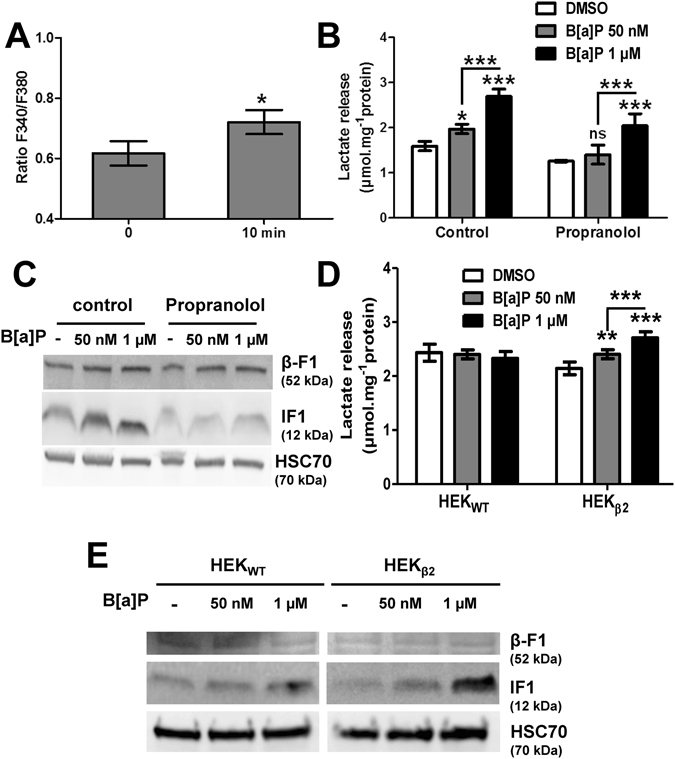
B[a]P-induced IF1 induction could occur through β2-adrenergic pathway stimulation. (A) Effects of B[a]P (50 nM) on calcium was assessed by microspectrofluorimetry after staining F258 cells with the Fura-2-AM probe. The ratio F340/F380 reflects intracellular Ca2+ concentration. *p < 0.05, DMSO vs B[a]P-treated cells. (B,C) F258 cells were pre-treated or not with the β-receptor inhibitor propranolol (10 µM) for 1 hour prior to co-exposure to B[a]P for 48 hours. The B[a]P-induced glycolytic shift (B) was investigated by monitoring extracellular lactate, and the IF1 protein level (C) was analyzed on total lysates by western blotting. A role for β2-adrenergic receptor in the B[a]P (50 nM or 1 µM, 48 h)-induced extracellular lactate (D) or total IF1 protein level (E), was evaluated in both HEKWT cells (not expressing β2-adrenergic receptor), and HEKβ2 (in which the receptor is overexpressed). HSC70 was used as loading control. Number of independent experiments = 3 for all conditions. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, DMSO vs B[a]P-treated cells, unless otherwise quoted.
