Figure 1.
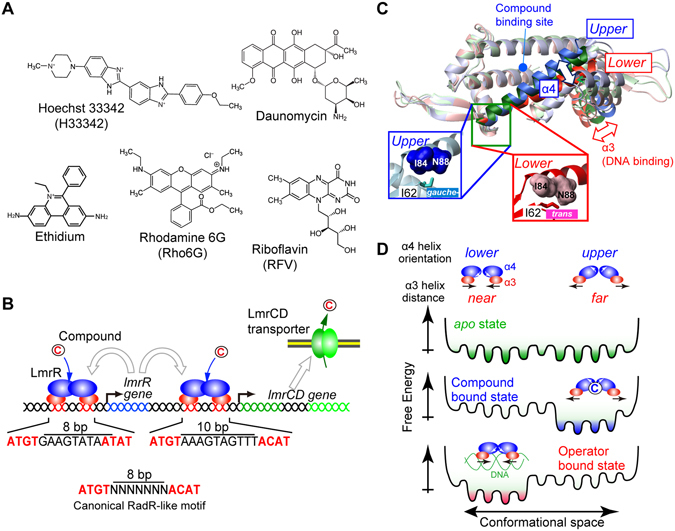
Ligands, regulatory mechanism, and structural properties of LmrR. (A) Chemical structures of compounds that are able to bind to LmrR. (B) Schematic representation of gene regulation by LmrR. LmrR regulates the transcription of both the lmrR and lmrCD genes by binding to their respective operator regions. White arrows indicate the destinations of proteins that are translated from each gene. (C) Different orientations of the C-terminal α4 helix. A superposition of the LmrR dimer structures is shown (3F8C, blue; 3F8B, green; 3F8F, red). Inset: close-up view of the hinge region. The Ile62 χ2 angle is defined by the α4 helix orientation. The α4 helix orientations are coupled to the distance between the α3 helices. (D) Schematic representation of the LmrR conformational equilibrium in the apo, compound-bound, and DNA-bound states, which underlies the reciprocal compound/operator binding by LmrR.
