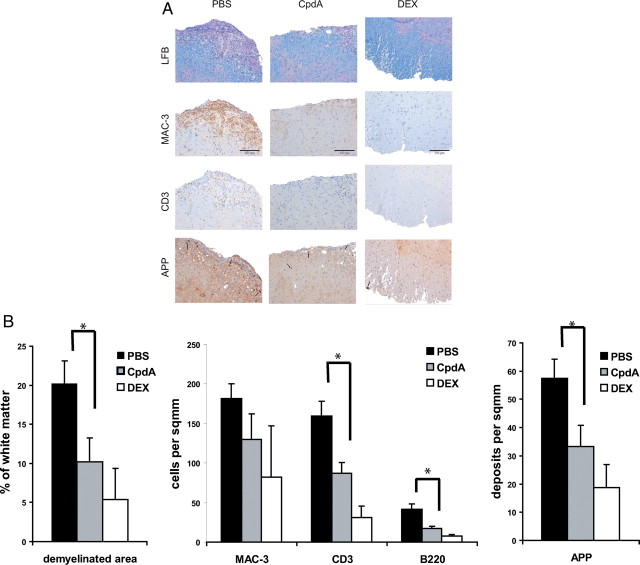
Fig. 2.
Reduced inflammation and demyelination in the CNS of CpdA-treated mice. PBS, CpdA, and DEX was administered every second day from the onset of acute disease (d 10 after immunization). A, Histological profiles of spinal cords from PBS-, CpdA-, and DEX-treated mice 25 d after EAE induction. Sections from the lumbar spinal cord were examined for infiltrating macrophages (MAC3, brown) and T cells (CD3, brown) by immunohistochemistry, demyelination by LFB (blue) staining, and axonal damage by APP (brown) immunohistochemistry. Scale bar, 100 μm. B, Quantification of spinal cord infiltrates, demyelination, and axonal damage from histological sections shown in panel A. Numbers of infiltrating T cells (CD3), B cells (B220), and macrophages (MAC3) in PBS-, CpdA-, and DEX-treated mice after EAE induction. Results are displayed as mean values ± sem. *, P < 0.05 (PBS vs. CpdA).