Figure 3.
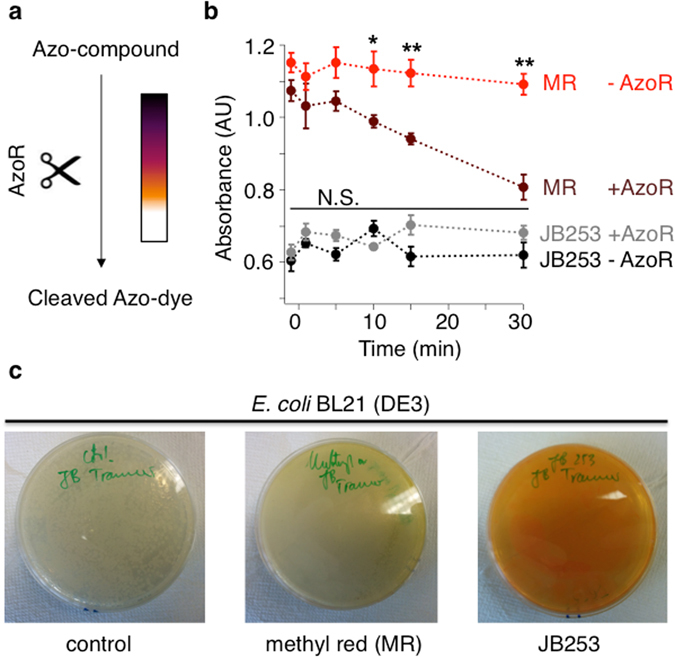
Assessing azo-compound cleavage by azoreductase. (a) The bacterial enzyme azoreductase (AzoR) reductively cleaves deeply-colored azo-compounds into corresponding colorless anilines. (b) AzoR derived from E. coli BL21 (DE3) is able to cleave the azo-dye Methyl Red (MR; λ = 430 nm), but not the AzoSulfonylurea JB253 (λ = 450 nm) (n = 4). (c) E. coli BL21 (DE3) on Agar plates after control (left), MR (middle) and JB253 (right) incubation shows that JB253 is still present while MR almost completely disappears; (n = 4). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 or NS, non-significant, MR or JB253 − AzoR versus MR or JB253 + AzoR; two-way ANOVA (Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test). Values represent mean ± SEM.
