Figure 2.
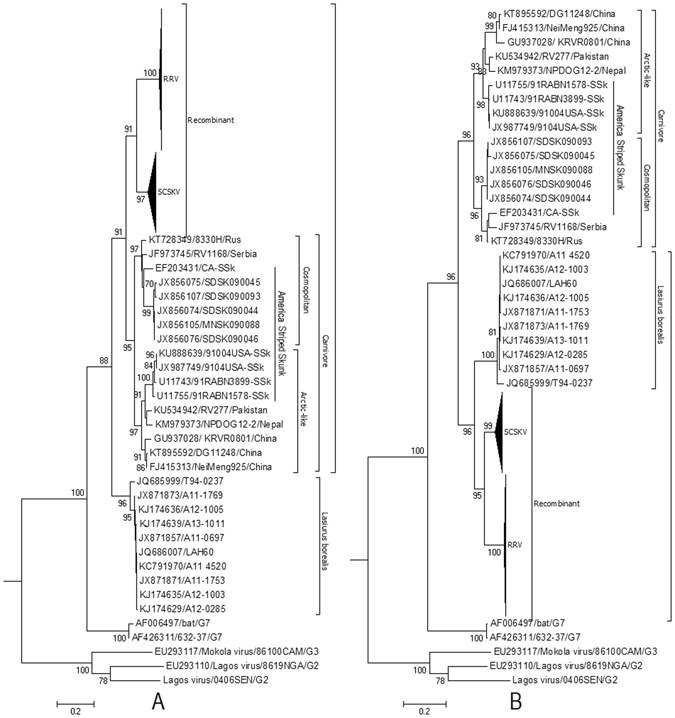
Phylogenetic patterns of the different regions of the G gene delimited by the putative breakpoints. (A) Phylogenetic history of the G gene region from positions 601 to 1347. (B) Phylogenetic history of G gene regions from positions 1 to 600 and 1347 to 1515 of the alignment. The evolutionary history was inferred using maximum likelihood (ML) methods. Bayesian Information Criterion within MEGA6 was used to find the best nucleotide substitution model for ML analyses. ML trees were constructed using the Tamura 3-parameter nucleotide substitution model. Among-site rate variation was gamma-distributed with invariant sites (G + I) (A) or gamma-distributed (G) (B) with four rate categories (Γ4). Bootstrap values (>70%) are listed above the branches. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA v6. G2, G3, and G7 indicate genotypes 2, 3, and 7 of Lyssavirus; NCSK, north-central skunk; SCSK, south-central skunk; Rac, raccoon. Cosmopolitan and Arctic-like RABVs are also included.
