Figure 5.
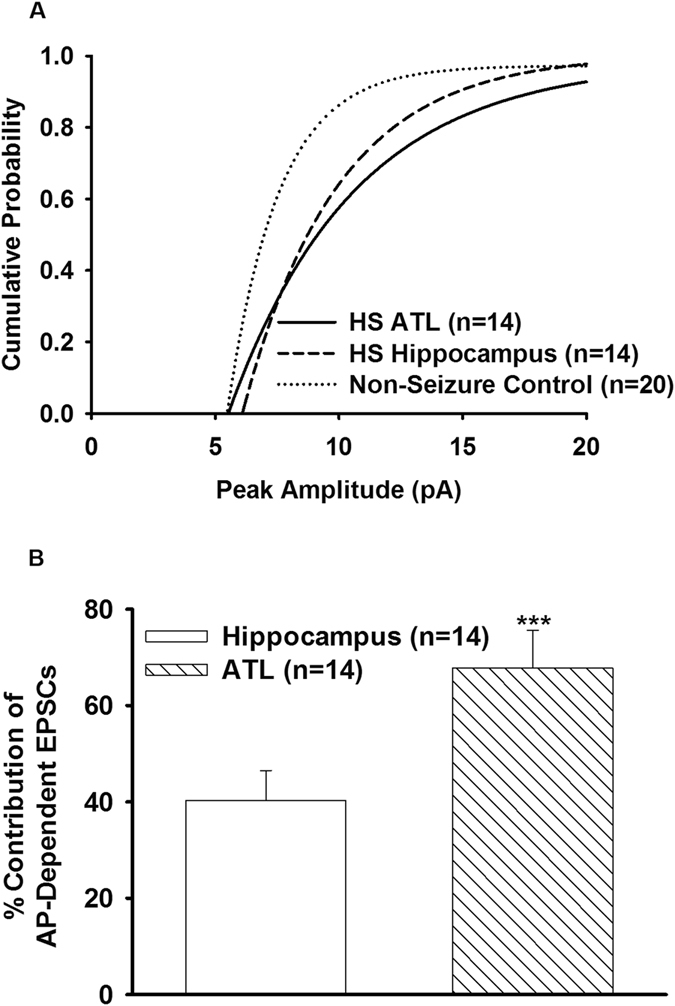
Contribution of action potential-dependent spontaneous EPSCs in the hippocampal and ATL samples. (A) Cumulative distribution of peak amplitude of mEPSCs recorded from non-epileptic control and the hippocampal and ATL samples of HS. In comparison to non-epileptic control, the cumulative distribution of peak amplitude of the hippocampal and ATL samples was displaced to the right (p = 0.03 for the hippocampal; p = 0.003 for ATL according to K-S test). (B) Graph shows the percent contribution of AP-dependent EPSCs in MTLE samples with respect to non-seizure control after bath application of TTX (200 nM, 10 min). Data were obtained from twenty neurons from twenty patients for non-seizure control, fourteen neurons from the hippocampal samples of fourteen HS patients and sixteen neurons from the ATL samples of fourteen HS patients. The magnitude of reduction in the frequency of spontaneous EPSCs caused by TTX in the ATL samples was significantly larger than that in case of the hippocampal samples. (***p = 0.0007 according to one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test).
