Figure 5.
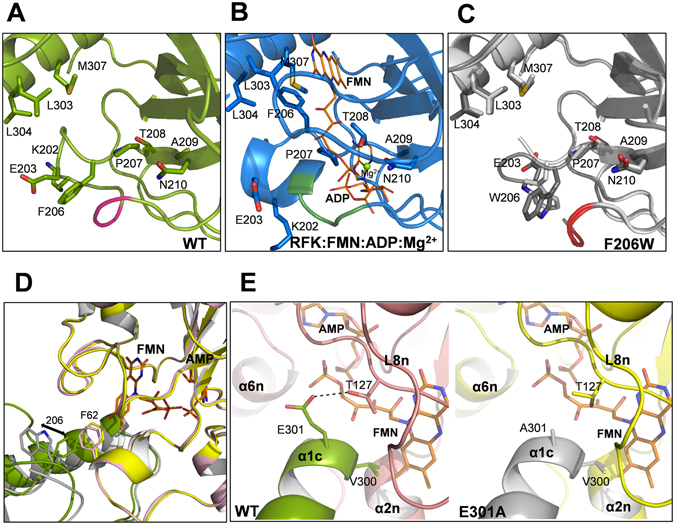
Structural analysis of CaFADS variants. Detail of the RFK module around the F206 position in (A) WT CaFADS (PDB code: 2x0k) (green), (B) the WT CaFADS ternary complex with the reaction products (PDB code: 5a89) (blue) and (C) superposition of the two chains of the asymmetric unit (Chain A in light gray and Chain B in dark gray) in F206W CaFADS with the two different conformations adopted by W206 (PDB code: 5fnz). Relevant residues are represented in sticks and CPK colored, and residues 197, 198 and 199 of L1c-FlapI are highlighted in pink, green and red, respectively. FMN and ADP ligands of the ternary complex are depicted as narrow sticks with orange carbons and the Mg2+ ion is shown as a green sphere. (D) Superposition of predicted macromolecular head-to-tail interfaces at the RFK and FMNAT modules of contiguous protomers within each trimer in WT CaFADS (modules in green and pink, respectively) and in F206W CaFADS (modules in gray and yellow, respectively). Residues 62 and 206 are shown in colored sticks. An arrow indicates the change in side chain conformations at position 206 in the mutant. (E) Detail of the predicted trimer head-to-tail interface region around position 301 in WT (left panel, RFK module in green and FMNAT module in pink) and E301A (right panel, RFK module in gray and FMNAT module yellow, respectively) CaFADS variants. In (D,E) FMN and AMP ligands in the FMNAT module have been modelled as previously described and are shown in sticks colored with carbons in orange6.
