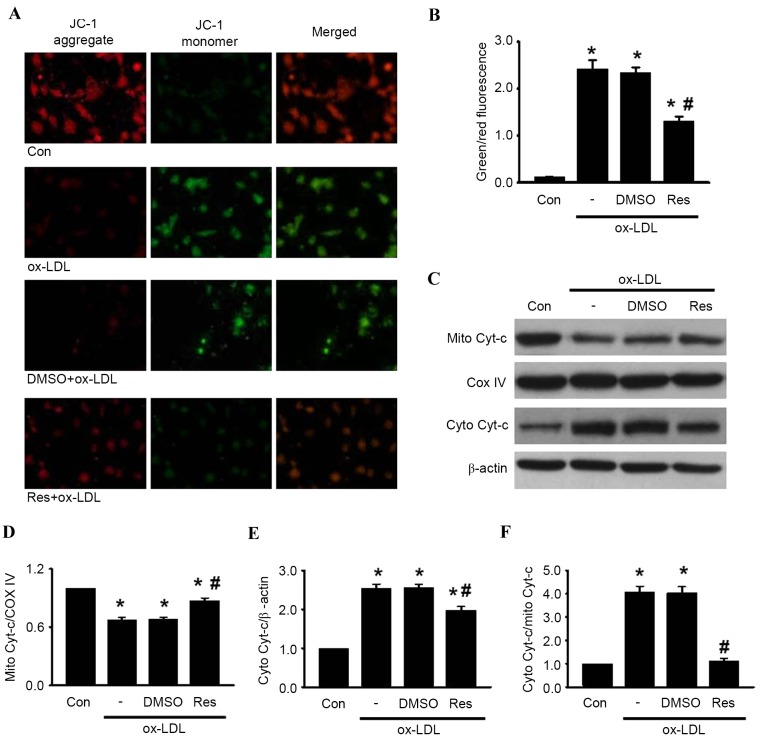
Figure 3.
Res inhibits ox-LDL-induced apoptosis in HUVECs through the mitochondria-dependent pathway. HUVECs were treated with ox-LDL (120 µg/ml) in the presence or absence of Res (40 µg/ml) for 24 h. (A) Mitochondrial membrane potential was measured using JC-1 dye staining under confocal microscopy. Green fluorescence represents JC-1 monomer and red fluorescence represents JC-1 aggregate; merged images show combined green and red images (x400). (B) Quantitative analysis of the ratio of green/red fluorescence (C) Protein expression of cytochrome c in mitochondria and cytosol were measured using western blot analysis. Densitometric analyses of the expression of cytochrome c in the (D) mitochondria and (E) cytosol. (F) Densitometric analysis of the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm. All data are presented as the mean + standard error of the mean. *P<0.05, vs. control; #P<0.05 m vs. ox-LDL group (n=4–6). HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; ox-LDL, oxidized-low density lipoprotein; Res, resveratrol; Con, control; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; JC-1, 5,5′, 6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′, 3,3′-tetraethyl-benza-midazolocarbocyanin iodide; Mito, mitochondrial; Cyto, cytosolic; Cyt-c, cytochrome c; COX IV, cyclooxygenase IV.