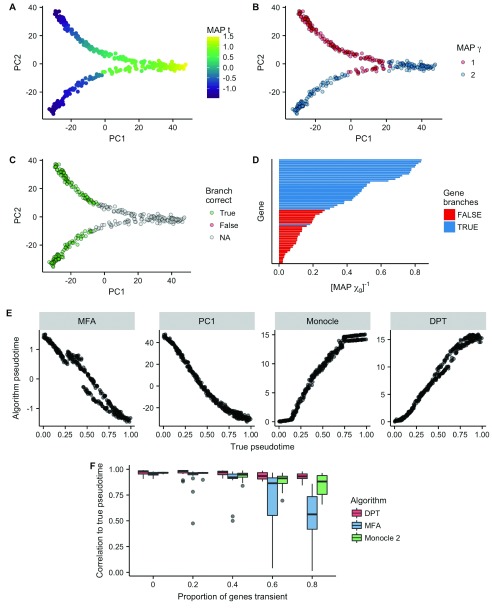
Figure 2. Probabilistic inference of bifurcations in synthetic data.
A Principal component analysis representation of a toy dataset for 300 cells and 60 genes, colored by the maximum a posteriori (MAP) pseudotime estimates. B Equivalent representation as ( A) color by the MAP branch estimate. C Equivalent representation showing whether each branch was assigned correctly. Due to the non-identifiability of mixture components, we map component indices from true to inferred such that the agreement is maximized. D The inverse MAP estimates of χ largely identify which genes in the dataset exhibit different behavior across the two branches. E Comparison of different pseudotime inference algorithms to the ground truth pseudotime on this particular dataset. The algorithms MFA, PC1 (principal component 1), Monocle and DPT had correlations of 0.98, 0.98, 0.98, 0.99 (to 2 s.f.), respectively. F The correlation of inferred pseudotimes to ground truth depending on the proportion of genes in the dataset exhibiting transient behavior. MFA shows competitive performance up to around 40% of genes begin transient despite an inherent linear assumption.