Figure 2.
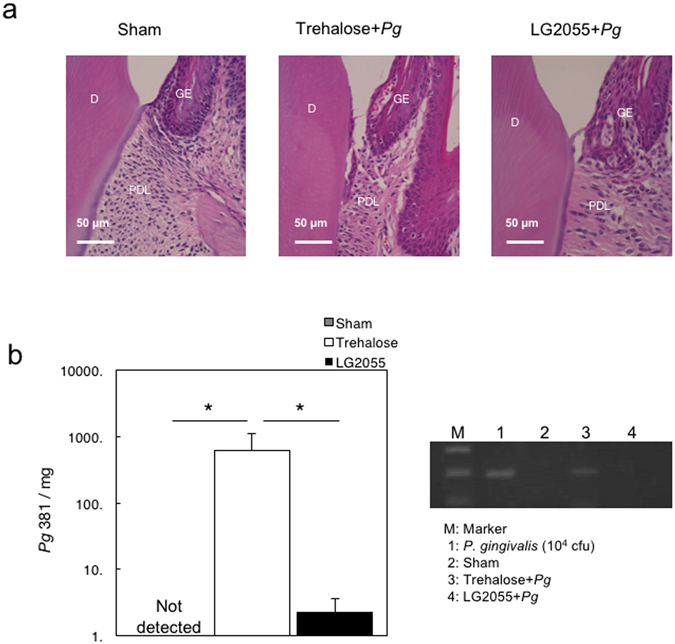
Suppression of P. gingivalis-induced detachment and disorganization of the periodontal ligament, and bacteria detection by gastric intubation with LG2055. (a) Histochemical analysis of gingival tissue. Thirty days after P. gingivalis infection, mouse lower jaws with gingival tissue were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. D: dentin, GE: gingival epithelium, PDL: periodontal ligament. (b) Detection of P. gingivalis-specific 16 S rRNA. Thirty days after P. gingivalis infection, DNA was extracted from gingival tissues of mice and amplified using real-time quantitative PCR with a pair of primers corresponding to P. gingivalis-specific 16 S rRNA. Different numbers of DNA from P. gingivalis 381 were used to generate a standard curve. All values are expressed as the means ± SEM per mg of tissue for eight mice per group; *p < 0.05.
