Figure 4.
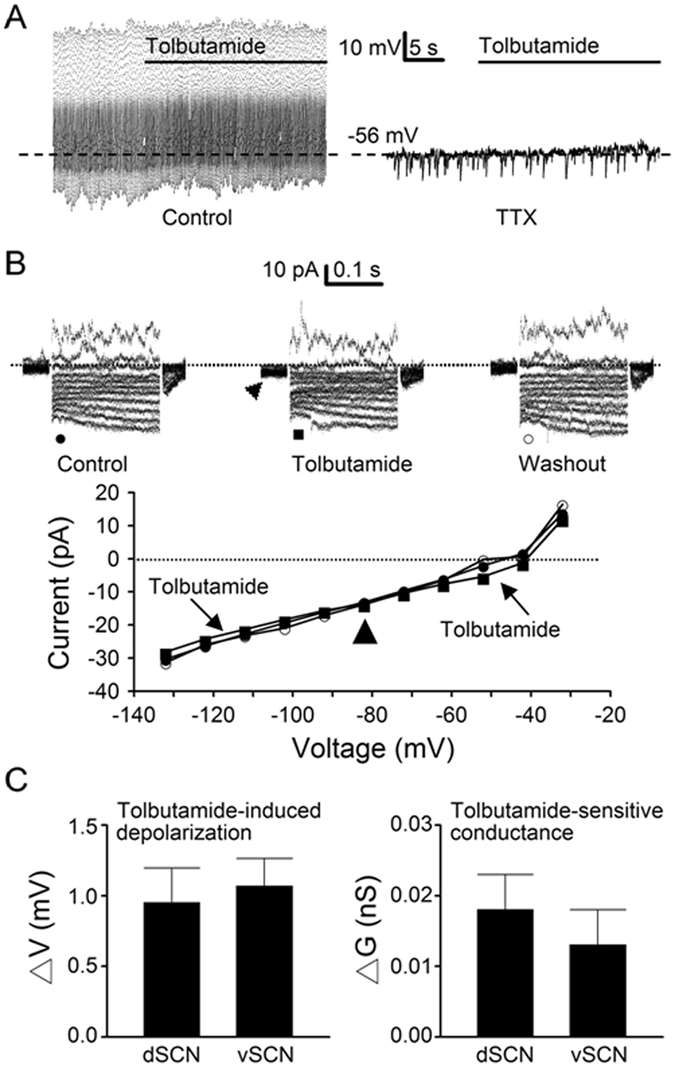
Tolbutamide effects on membrane potential and conductance with perforated patch recordings. (A) A representative dSCN neurone showing the effects of tolbutamide on spontaneous firing (left panel) and membrane potential (right panel) after the addition of TTX to block action potentials. Note the weak depolarisation by tolbutamide. Daytime recordings (ZT 7). (B) A representative dSCN neurone showing the reversible effects of tolbutamide on the membrane current (top panels) and the I-V relations (bottom panel). Note the small inward current induced by tolbutamide at a holding potential of −52 mV (marked by arrowhead). Nighttime recordings (ZT 13). (C) Summary of tolbutamide-induced depolarisation (left panel) and tolbutamide-sensitive conductance (right panel). Baseline resting potential: dSCN (−56 ± 1 mV; n = 39), vSCN (−56 ± 1 mV; n = 39). Baseline resting conductance: dSCN (0.38 ± 0.05 nS; n = 17), vSCN (0.31 ± 0.04 nS; n = 17). Dotted lines are zero current levels.
