Figure 3.
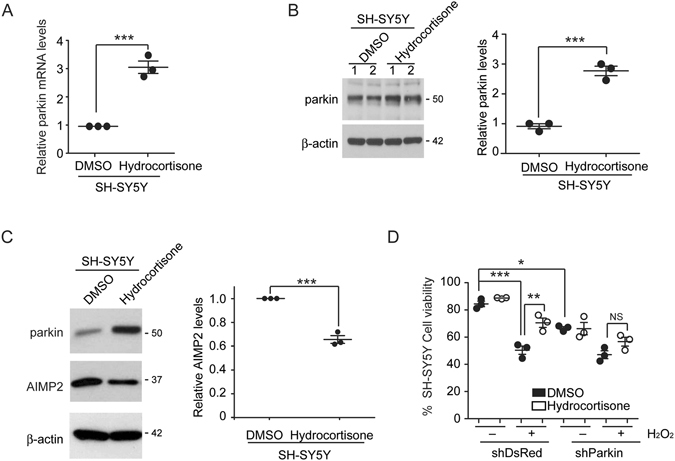
Hydrocortisone’s protection of SH-SY5Y cells is parkin dependent. (A) Parkin mRNA levels in SH-SY5Y cells induced by hydrocortisone (10 µM) treatment were normalized to the level of GAPDH based on real time quantitative PCR (n = 3). (B) Western blot analysis of parkin expression in SH-SY5Y cells treated with hydrocortisone or DMSO control (left panel). Relative parkin protein levels in SH-SY5Y cells treated with hydrocortisone or DMSO (right panel, n = 3) were normalized to that of β-actin. (C) Western blot analysis of parkin and its toxic substrate AIMP2 in SH-SY5Y cells treated with hydrocortisone or DMSO control (left panel). β-actin was used as an internal loading control. Relative AIMP2 protein levels (right panel, n = 3) were normalized to that of β-actin. (D) Viability of SH-SY5Y cells transiently transfected with shRNA to parkin or DsRed as control. Two days after transfection, SH-SY5Y cells were pretreated with hydrocortisone or DMSO and challenged with H2O2 (1 mM, 16 hrs). Cell viability was assessed by trypan blue exclusion assay (n = 3). Quantified data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test (A,B,C) or nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA test (D). Full blots (for cropped images in B,C) are presented in Figure S6.
