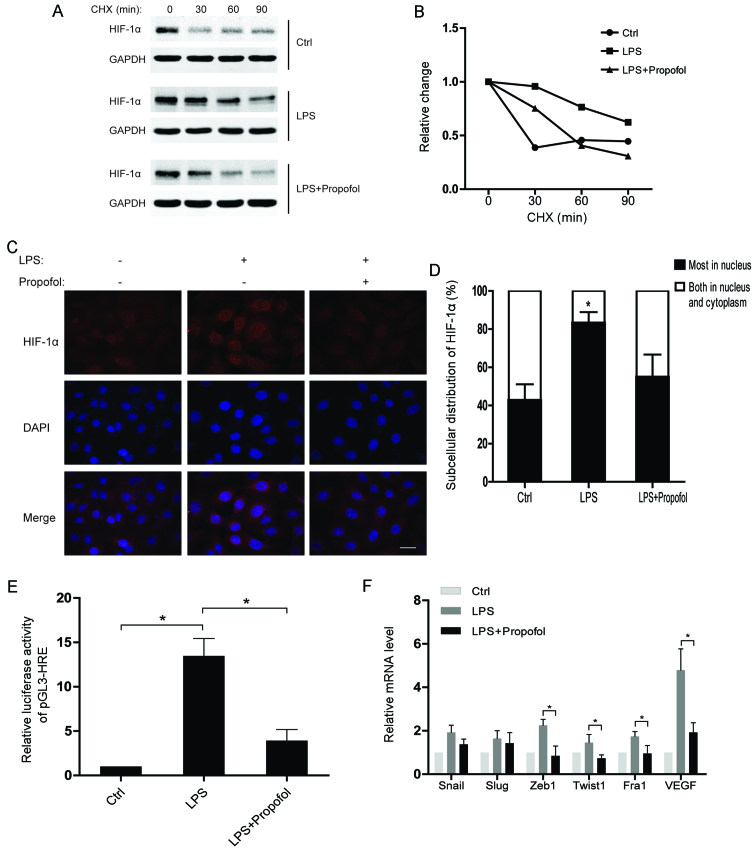
Figure 3.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced protein stability and nuclear accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) is attenuated by propofol. (A) A549 cells were pretreated with 10 µg/ml LPS or 20 µg/ml propofol for 12 h and then treated with 10 µg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated times. Whole-cell lysates were harvested and analyzed by western blot analyses. (B) Densitometric analysis of data from (A) using ImageJ to determine the stability of HIF-1α. (C) Immunofluorescent staining for HIF-1α in A549 cells exposed to the indicated reagents for 12 h (scale bar, 20 µm). (D) The pattern of nucleocytoplasmic distribution of HIF-1α in C was quantified. The number of cells was determined and is presented as the percentage of the total population. A minimum of 100 cells was counted for each experiment and data are presented as means ± SD from 3 independent experiments; *P<0.05, compared with the control or LPS + propofol group. (E) A549 cells were transfected with a pGL3-HRE plasmid which contains 3 repeated HREs. The transcriptional activity of HIF-1α was measured after treating the A549 cells with the indicated reagents; *P<0.05. (F) Relative mRNA levels of EMT-TFs and VEGF in A549 cells treated with the indicated reagents. The mRNA levels of the indicated genes were normalized to actin; *P<0.05. EMT-TFs, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-transcription factors.