Figure 3. Compound A reduces donor Tcon accumulation within recipient organs after transplant and in particular the host lung.
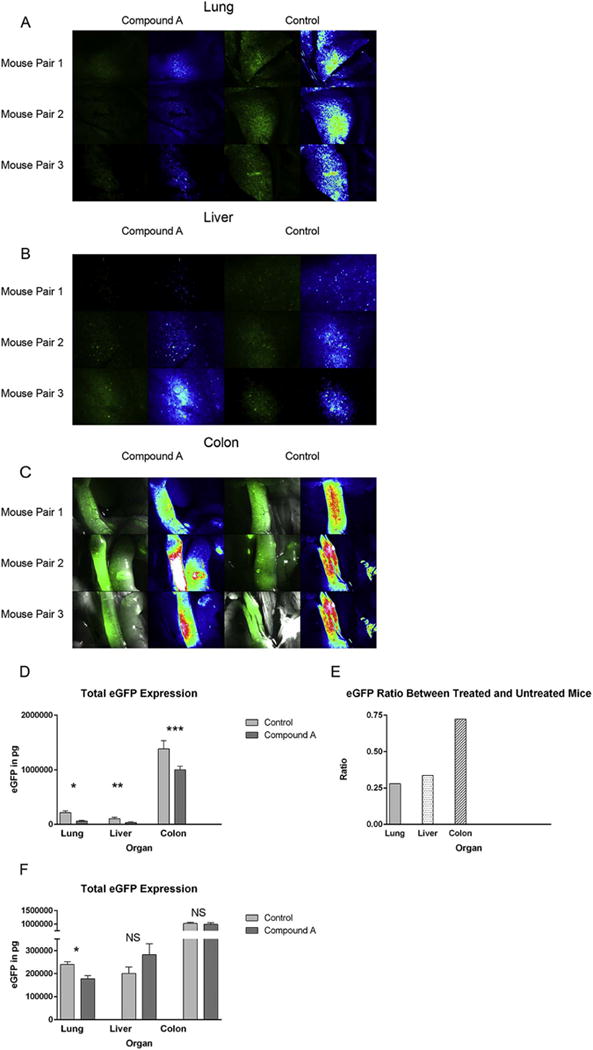
(A–E) B6D2 mice were lethally irradiated to 950 rads on transplant day −1 and then administered 3×106 WT B6 TCD BM cells plus 4×106 CD25-depleted whole Tcons obtained from eGFP+ B6 mice +/− Compound A dosed at 250mcg once daily by IP injection on transplant days 0–5. On transplant day +7, recipient mice were killed and their organs imaged by fluorescence stereomicroscopy (A–C). For each image, actual eGFP fluorescence is depicted on the left and a rainbow feature is shown on the right to indicate the strength of the eGFP signal (white>red>yellow>green>blue>black). Three untreated controls and three mice given Compound A were imaged. (D) Host organs were subsequently removed and homogenized, and total eGFP levels then measured in each organ by anti-eGFP ELISA. n=6 mice per treatment group. *P=0.0012 for total pulmonary eGFP comparison between control and Compound A groups by Student’s t test. **P=0.048. ***P=0.0355. (E) Mean organ eGFP level ratios between treated and untreated mice are also depicted. (F) B6D2 mice were lethally irradiated to 950 rads on day −1 and then administered 3×106 WT B6 TCD BM cells plus 4×106 CD25-depleted whole Tcons obtained from eGFP+ B6 mice +/− Compound A dosed at 100mcg once daily by IP injection on transplant days 0–7. On transplant day +7, recipient mice were killed and their organs removed and homogenized. Total eGFP levels were then measured for each organ by anti-eGFP ELISA. *P=0.0082.
