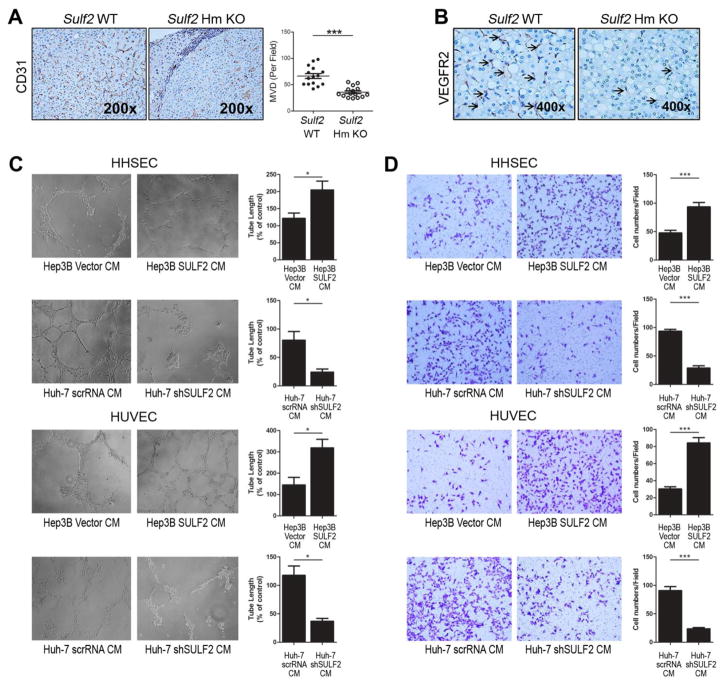
Figure 2. SULF2 expression promotes angiogenesis in HCCs.
A. DEN-induced HCCs from Sulf2 Hm KO mice had decreased MVD compared to tumors from Sulf2 WT mice, as shown by CD31 immunohistochemical staining (left panel, 200×) and quantification of tumor microvascular density (right panel). For quantification of MVD, CD31-positive cells were identified by a brown precipitate in the cytoplasm of endothelial cells; vessels in each section were counted in five microscope fields. B. VEGFR2 immunohistochemical staining of HCC tumors from DEN-induced Sulf2 WT and Sulf2 Hm KO mice showed increased staining in Sulf2-expressing tumors (400×). Tumor tissues were fixed in formalin, embedded in paraffin, sectioned and stained with antibody against VEGFR2. C and D. Tube formation (C) and chemotaxis (D) of HHSECs and HUVECs, measured after 12 hours treatment with conditioned medium (CM) from high SULF2-expressing Hep3B or low SULF2-expressing Huh-7, showed that the expression status of SULF2 in the CM can affect tumor angiogenesis. *P< .05; **P< .01; ***P< .001.