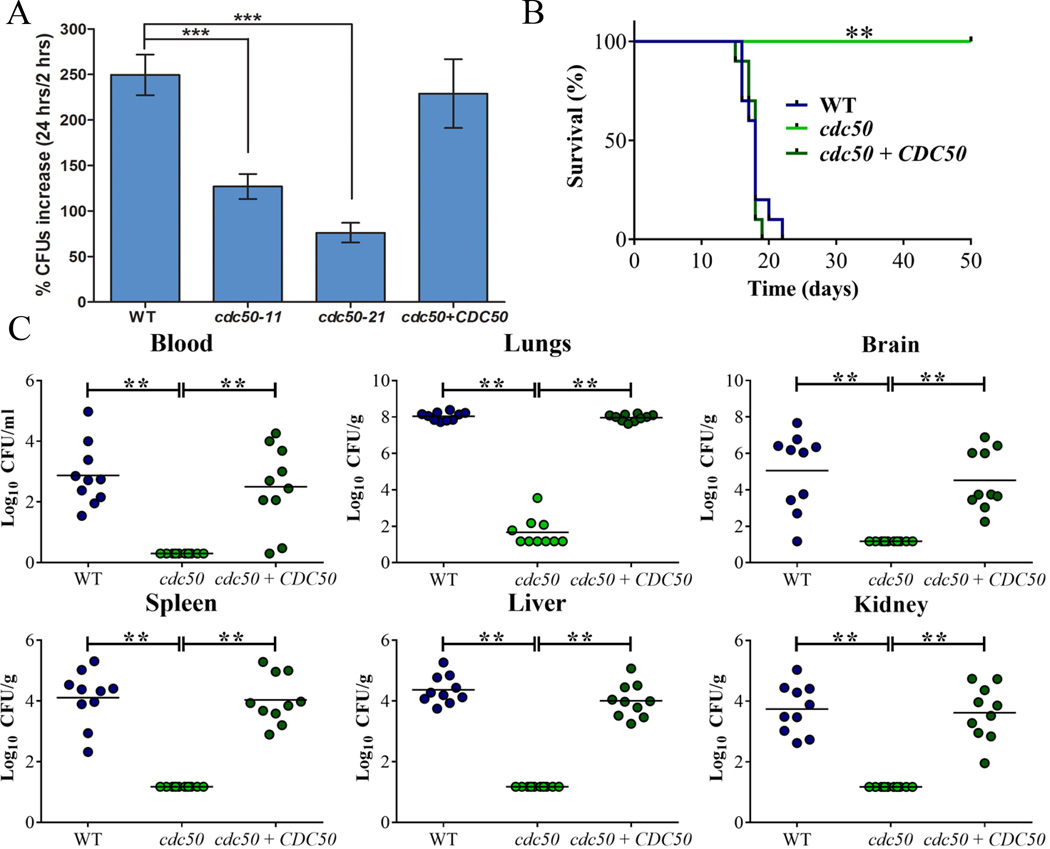
Figure 2. Cdc50 is required for survival in macrophages and for virulence in mice.
A) Cells of the WT strain, two cdc50 mutants, and the CDC50 complemented strain were incubated with macrophage J774A.1 cells. C. neoformans was inoculated at 1 × 105 cells, and the wells were washed after 2 h of incubation to remove extracellular yeast cells. Fungal proliferation was measured by plating on YPD and counting CFUs after 24 h of incubation. The data represent the mean values ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M) of three independent biological experiments done in triplicate. Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test to determine the difference between the WT strain and two cdc50 mutants, separately (***P < 0.0005, significantly different). B) Ten female BALB/c mice were inoculated intranasally with 2 × 105 cells of each of the strains indicated, and the survival of the mice was monitored daily. The cdc50-11 mutant was used for the experiment. Survival differences between groups of mice were evaluated by log rank tests. The P values for the mice infected with the WT and mutant strains were statistically significantly different (P < 0.001). C) Fungal burden was determined in systemic organs (lung, brain, liver, kidney and spleen) and cardiac blood for all mice infected with the strains at the end of the experiment. The Mann-Whitney U test was used for statistical analysis. Differences in the fungal loads between the WT and cdc50 mutants in each organ examined were statistically significant (P < 0.001).