Table 4.
Examples of pharmacologically relevant classes of flavonoids
| Class | Basic structure | Typical rich food source | Example | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavanolsa |
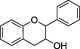
|
Soy flour, red wine, green tea, grape, wine, cocoa, apricot, beans | Catechin, epicatechin | The intake of flavanol‐rich foods (such as Cocoa flavonols) has been evaluated in relation to cardiovascular healthb |
| Flavanones |
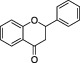
|
Citrus fruits (Tomás‐Barberán and Clifford, 2000) | Hesperetin, Naringenin | Flavanones and flavanones‐rich botanical extracts have been a subject of great interest for scientific research for as a possible emerging treatment for diabetes and its complications and cardiovascular protectionc |
| Flavones |
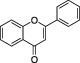
|
Green leafy spices, for example, Parsley | Apigenin, Luteolin | Flavones can contribute to plant tissue colour, if they occur in high concentrations or are complexed with metal ions. Flavones participate in taste. |
| Flavonols |
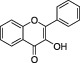
|
Nearly ubiquitous in foods, for example, quercetin. Main sources include yellow onion, curly kale and leek. | Kaempferol, Myricetin Quercetin | The most abundant flavonoid assumed with the diet is the flavonol quercetin |
| Isoflavonoids |
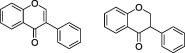
|
Soybeans, soy foods and legumes | Daidzein, Genistein | lsoflavonoids are a distinct class of flavonoids with estrogenic activity. They are found almost exclusively in legumes, particularly soybeans. Isoflavonoid‐containing preparations are promoted for alleviating menopausal symptoms |
| Proanthocyanidins |
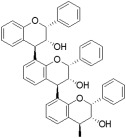
|
The foods with the highest levels of total proanthocyanidins are, in decreasing order, ground cinnamon, sorghum (sumac bran), dry grape seed, unsweetened baking chocolate, raw pinto beans, sorghum (high‐tannin whole grain), choke berries, red kidney beans, hazelnuts and pecan nutsd | Pycnogenol proanthocyanidin A‐2 (in hawthorn berry) | Also named condensed tannins, represents the most abundant plant‐derived polyphenols. Proanthocyanidins are responsible for the astringent taste of fruits. Potential areas of medical interest include the prevention of cardiovascular and metabolic disorders. |
| Anthocyanidins |
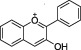
|
Red, purple and blue Berries (e.g. blackberry, strawberry, blueberry), aubergine, red wine |
Cyanidin, Delphinidin, peonidin | Anthocyanins produce the blue and red coloration of berry fruits, cherries and plums, eggplant, red cabbage and radishes. Fruit anthocyanins content usually increases as the fruit matures |
General information, including chemistry and occurrence, has been extracted from Peterson and Dwyer (1998); Samuelsson (1999); Beecher (2003); Manach et al. (2004); D'Archivio et al. (2007); Cui and Duke (2015);
Flavanols may exist both as monomer (catechins) and polymer (proanthocyanidins) form;
Chanet et al. (2012);
