Fig. 7.
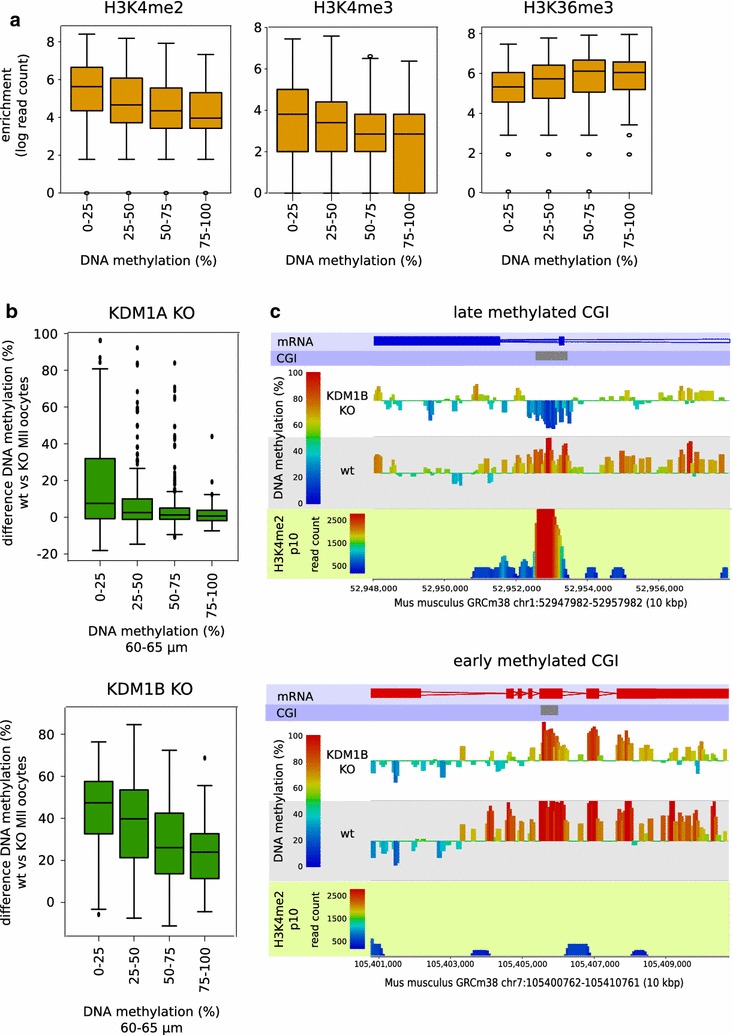
CpG island methylation kinetics in relation to chromatin parameters. a Box whisker plots showing enrichment (log-transformed corrected read count) of H3K4me2, H3K4me3 and H3K36me3 at CGIs in relation to DNA methylation in 60–65 µm oocytes (PBAT data). The ChIP-seq data shown are from p10 oocytes; similar trends were observed in ChIP-seq data from e18.5 oocytes. Pearson’s correlation coefficients are: −0.293 for H3K4me2, −0.173 for H3K4me3, 0.240 for H3K36me3. The numbers of CGIs analysed in each methylation category (from lowest to highest) were: 464, 327, 382 and 63. b Box whisker plots showing the degree of DNA methylation change at CGIs in Kdm1a- and Kdm1b-null MII oocytes in relation to methylation in 60–65 µm oocytes. Pearson’s correlation coefficients are: −0.296 for Kdm1a and −0.357 for Kdm1b. The numbers of CGIs analysed in each methylation category (from lowest to highest) were: 244, 185, 255 and 28 for Kdm1a, and 270, 199, 268 and 31 for Kdm1b. c Browser screenshots of a representative early-methylating and late-methylating CGI (84.2 and 12.2% methylation in 60–65 µm oocytes, respectively) in relation to p10 H3K4me2 enrichment and DNA methylation attained in wild-type (WT) or Kdm1b-null MII oocytes
